CCNY researchers announce photon-phonon breakthrough
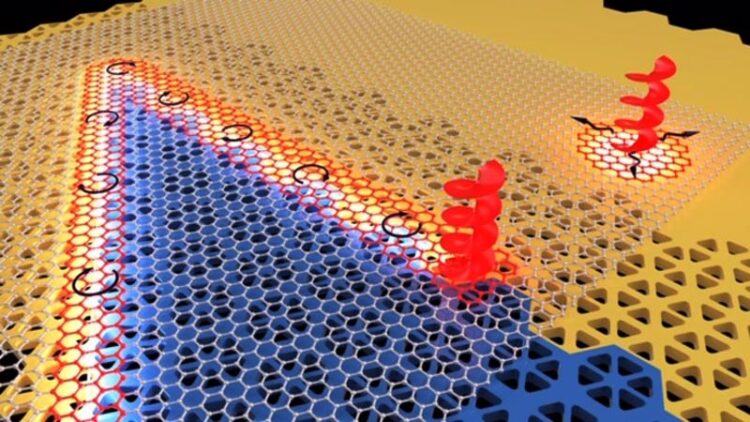
Topologically distinct photonic crystals (orange and blue) with a layer of hexagonal boron nitride on top enable coupling of topological light and lattice vibrations to form chiral half-light half-vibration excitations, which can be directionally guided along 1D channels in robust manner.
Image credit: Filipp Komissarenko and Sriram Guddala
New research by a City College of New York team has uncovered a novel way to combine two different states of matter. For one of the first times, topological photons—light—has been combined with lattice vibrations, also known as phonons, to manipulate their propagation in a robust and controllable way.
The study utilized topological photonics, an emergent direction in photonics which leverages fundamental ideas of the mathematical field of topology about conserved quantities—topological invariants—that remain constant when altering parts of a geometric object under continuous deformations. One of the simplest examples of such invariants is number of holes, which, for instance, makes donut and mug equivalent from the topological point of view. The topological properties endow photons with helicity, when photons spin as they propagate, leading to unique and unexpected characteristics, such as robustness to defects and unidirectional propagation along interfaces between topologically distinct materials. Thanks to interactions with vibrations in crystals, these helical photons can then be used to channel infrared light along with vibrations.
The implications of this work are broad, in particular allowing researchers to advance Raman spectroscopy, which is used to determine vibrational modes of molecules. The research also holds promise for vibrational spectroscopy—also known as infrared spectroscopy—which measures the interaction of infrared radiation with matter through absorption, emission, or reflection. This can then be utilized to study and identify and characterize chemical substances.
“We coupled helical photons with lattice vibrations in hexagonal boron nitride, creating a new hybrid matter referred to as phonon-polaritons,” said Alexander Khanikaev, lead author and physicist with affiliation in CCNY’s Grove School of Engineering. “It is half light and half vibrations. Since infrared light and lattice vibrations are associated with heat, we created new channels for propagation of light and heat together. Typically, lattice vibrations are very hard to control, and guiding them around defects and sharp corners was impossible before.”
The new methodology can also implement directional radiative heat transfer, a form of energy transfer during which heat is dissipated through electromagnetic waves.
“We can create channels of arbitrary shape for this form of hybrid light and matter excitations to be guided along within a two-dimensional material we created,” added Dr. Sriram Guddala, postdoctoral researcher in Prof. Khanikaev’s group and the first author of the manuscript. “This method also allows us to switch the direction of propagation of vibrations along these channels, forward or backward, simply by switching polarizations handedness of the incident laser beam. Interestingly, as the phonon-polaritons propagate, the vibrations also rotate along with the electric field. This is an entirely novel way of guiding and rotating lattice vibrations, which also makes them helical.”
Entitled “Topological phonon-polariton funneling in midinfrared metasurfaces,” the study appears in the journal Science.
Journal: Science
Method of Research: Meta-analysis
Subject of Research: Cells
Article Title: Topological phonon-polariton funneling in midinfrared metasurfaces
Article Publication Date: 7-Oct-2021
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…


