Chemists describe a new form of ice
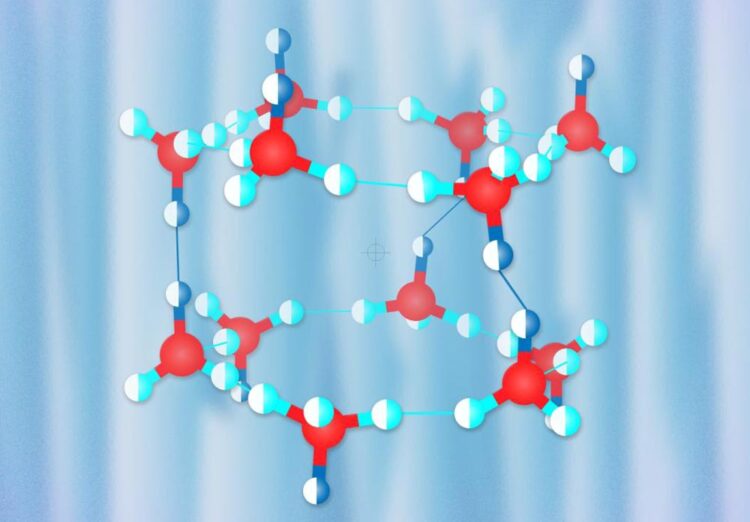
A novel hydrogen clathrate hydrate
Credit: Pavel Odinev / Skoltech
Scientists from the United States, China, and Russia have described the structure and properties of a novel hydrogen clathrate hydrate that forms at room temperature and relatively low pressure. Hydrogen hydrates are a potential solution for hydrogen storage and transportation, the most environmentally friendly fuel. The research was published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
Ice is a highly complex substance with multiple polymorphic modifications that keep growing in number as scientists make discoveries. The physical properties of ice vary greatly, too: for example, hydrogen bonds become symmetric at high pressures, making it impossible to distinguish a single water molecule, whereas low pressures cause proton disorder, placing water molecules in many possible spatial orientations within the crystal structure.
The ice around us, including snowflakes, is always proton-disordered. Ice can incorporate xenon, chlorine, carbon dioxide, or methane molecules and form gas hydrates, which often have a different structure from pure ice. The vast bulk of Earth’s natural gas exists in the form of gas hydrates.
In their new study, chemists from the United States, China, and Russia focused on hydrogen hydrates. Gas hydrates hold great interest both for theoretical research and practical applications, such as hydrogen storage. If stored in its natural form, hydrogen poses an explosion hazard, whereas density is way too low even in compressed hydrogen. That is why scientists are looking for cost-effective hydrogen storage solutions.
“This is not the first time we turn to hydrogen hydrates. In our previous research, we predicted a novel hydrogen hydrate with 2 hydrogen molecules per water molecule. Unfortunately, this exceptional hydrate can only exist at pressures above 380,000 atmospheres, which is easy to achieve in the lab but is hardly usable in practical applications. Our new paper describes hydrates that contain less hydrogen but can exist at much lower pressures,” Skoltech professor Artem R. Oganov says.
The crystal structure of hydrogen hydrates strongly depends on pressure. At low pressures, it has large cavities which, according to Oganov, resemble Chinese lanterns, each accommodating hydrogen molecules. As pressure increases, the structure becomes denser, with more hydrogen molecules packed into the crystal structure, although their degrees of freedom become significantly fewer.
In their research published in the Physical Review Letters, the scientists from the Carnegie Institution of Washington (USA) and the Institute of Solid State Physics in Hefei (China) led by Alexander F. Goncharov, a Professor at these two institutions, performed experiments to study the properties of various hydrogen hydrates and discovered an unusual hydrate with 3 water molecules per hydrogen molecule. The team led by Professor Oganov used the USPEX evolutionary algorithm developed by Oganov and his students to puzzle out the compound’s structure responsible for its peculiar behavior.
The researchers simulated the experiment’s conditions and found a new structure very similar to the known proton-ordered C1 hydrate but differing from C1 in water molecule orientations. The team showed that proton disorder should occur at room temperature, thus explaining the X-ray diffraction and Raman spectrum data obtained in the experiment.
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…


