Cylindrical vector beam multiplexer/demultiplexer using off-axis polarization control
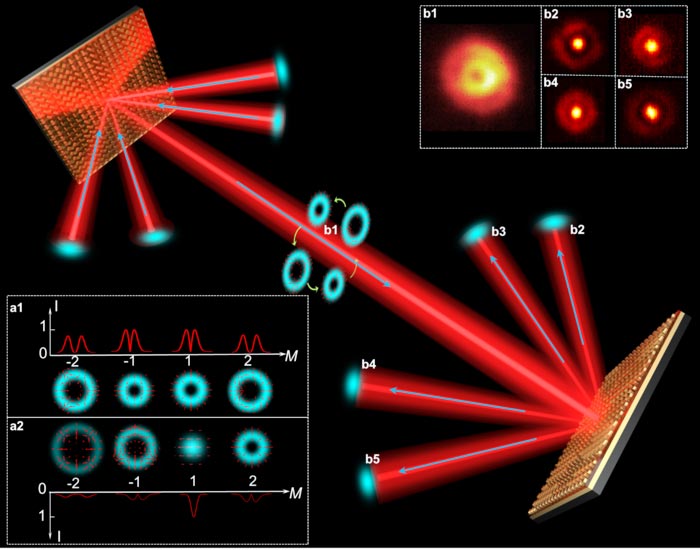
a1, Polarization and intensity distributions in each diffraction order with Gaussian beam incident, respectively. a2, Polarization and intensity distributions in each diffraction order with cylindrical vector beam (CVB) (m=-1) incident. b1, Measured coaxial CVB with 4 modes. b2-b5, Measured Gaussian points after demultiplexing of the different CVB mode channels.
Credit by Shuqing Chen, Zhiqiang Xie, Huapeng Ye, Xinrou Wang, Zhenghao Guo, Yanliang He, Ying Li, Xiaocong Yuan, and Dianyuan Fan
Cylindrical vector beam (CVB) multiplexing has emerged as a powerful technique to boost signal channels. Coupling and separating CVBs are two pivotal elements in CVB multiplexing communication. Although off-axis control technologies, such as miniature Dammann vortex gratings, have been investigated to couple and separate light beams, it is usually limited to light beams with homogeneous polarization due to its phase-only grating structure.
For CVBs with inhomogeneous polarization, a gradient phase device is required to create a gradient phase difference between the left- and right-handed circularly polarized (LHCP/RHCP) components, so that the CVBs with off-axis incident angles can coaxially propagate and carry different phase structures. Despite considerable efforts of off-axis control technologies, the off-axis polarization control of CVBs still remains a challenge.
According to Jones matrix analysis, CVB can be obtained by linearly superposing two orthogonal circularly polarized vortex beams with conjugate topological charges. After decomposed into LHCP and RHCP components, CVBs can be off-axis controlled by independently modulating the phase of these two components, and thus the mode coupling and separating can be achieved via introducing gradient phase changes. Optical metasurface is a kind of micro-nano optical device, which is capable of phase, amplitude, and polarization control by arranging the artificial nanoantenna. It shows that the metasurface enables circular polarization-dependent phase modulation by the spin-orbit interaction, which provides a route for independently phase control of two circularly polarized components.
Light Science & Application reports a new work from a team of scientists, led by Professors Dianyuan Fan, Xiaocong Yuan and Ying Li from Shenzhen University, China and co-workers. They have proposed an approach to realize off-axis polarization control for CVB multiplexing/demultiplexing based on a metal-dielectric-metal metasurface. The LHCP and RHCP components of CVBs were independently modulated via spin-to-orbit interactions by the properly designed metasurface, and then simultaneously multiplexed and demultiplexed due to the reversibility of light path and the conservation of vector mode.
More interestingly, the proposed multiplexers/demultiplexers are compatible with wavelength-division-multiplexing and polarization-division-multiplexing due to the broadband response and orthogonal polarization modulation. This study paves the way for CVB multiplexing/demultiplexing and may benefit high-capacity CVB communication.
Highlights:
a. Traditional phase-type grating devices are only suitable for off-axis control of uniform polarized beam. By combining the geometric phase and propagation phase in metasurface, they independently design the off-axis phase modulation for RHCP and LHCP components, which empowers the off-axis control of CVBs with nonuniform polarization distributions.
b. The vector mode is independent from wavelength and polarization state, which is expected to achieve hybrid-dimensional multiplexing communication. Since the proposed CVB multiplexer/demultiplexer based on off-axis polarization control shows a broadband response characteristic and orthogonal polarization response, it is compatible with wavelength-division-multiplexing and polarization-division-multiplexing.
DOI: 10.1038/s41377-021-00667-7
Article Title: Cylindrical vector beam multiplexer/demultiplexer using off-axis polarization control
Article Publication Date: 2-Nov-2021
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…


