Deep Insight Into Interfaces
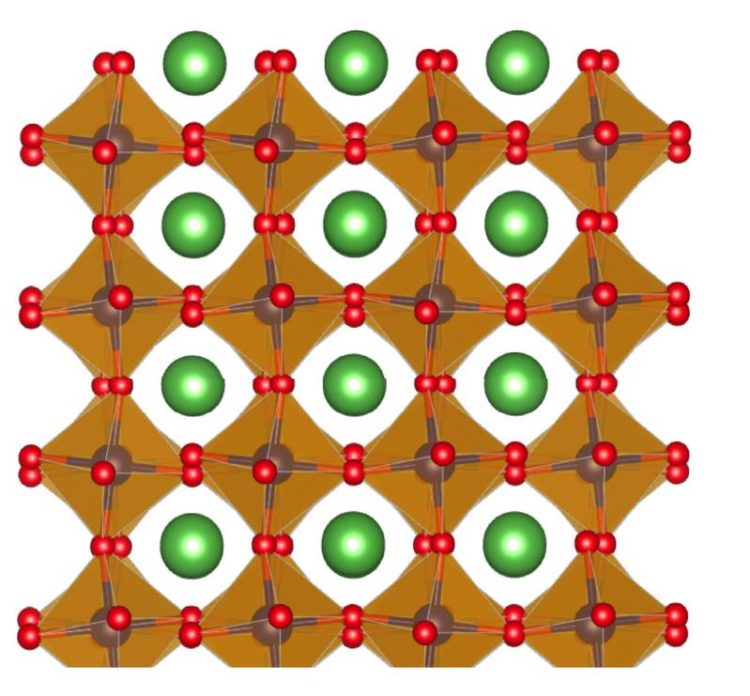
Film of lanthanum cobalt oxide shows a sequence of positively and negatively charged atomic layers. Without electronic reconstruction an enormous electrostatic field would form between the layers Graphic: J.E. Hamann-Borrero & Vladimir Hinkov
In his Nobel Lecture on December 8, 2000, Herbert Kroemer coined the saying “the interface is the device”. Kroemer referred to the mature field of semiconductor heterostructures, which form the basis of all modern electronics.
However, now, in the advent of novel, powerful devices based on the more complex and versatile topological and correlated materials, the statement is timelier than ever. Such materials are at the focus of research in the Department of Physics and Astronomy at Würzburg University: Currently, 16 groups are working in this field, and a Collaborative Research Center (CRC 1170) was established in 2015, which is funded by the German Science Foundation (DFG) with nearly 10 Million euro.
Publication in Nature Quantum Materials
In the recent years physicists from Würzburg University and coworkers from Germany, Canada, the U.S.A. and Korea developed a new method to uncover important charge properties of correlated oxide interfaces with unprecedented atomic scale resolution. The team of Professor Vladimir Hinkov and his coworkers report about this experimental method in the current issue of the Nature Journal “NPJ Quantum Materials”.
“Conventional electronic chips are based on networks of so-called p-n junctions, interfaces between semiconductors carrying positive and negative charges, respectively,” says Vladimir Hinkov, describing the background of this research. There are several drawbacks to such a setup: First, the junctions are thick, often of the order of hundreds of interatomic spacings. Second, operating the network requires the movement of many electrons, which costs a lot of energy due to electrical resistance. Third, semiconductors do not intrinsically have magnetic properties and their electron configuration is very basic. “This dramatically limits the ways to build functional junctions and to realize magnetic applications,” Hinkov reports.
Versatile properties require sophisticated methods
Transition-metal oxides, on the other hand, exhibit many different properties: Some of them are ferromagnetic, others are antiferromagnetic, and others in turn are high-temperature superconductors with very unconventional properties. Forming interfaces between such materials yields a plethora of phenomena, which hold promise for novel applications such as different sensors, lossless computer memory and ultrafast processors. The price one has to pay is that more sophisticated tools are necessary to study them: This is due to the variety of phenomena and due to the much shorter length scale, over which the properties of oxides change at such heterointerfaces, which is often just a few atomic spacings.
Of crucial importance is the behavior of electrons at the interface: Do they tend to accumulate? Which orbitals do they occupy, i.e. how do the electron clouds arrange around the atoms? Is there magnetic order, i.e. do the tiny magnetic moments of the electrons called spins align relative to each other, establishing magnetic order? Physicists around the world are seeking for answers to these questions.
Measurements on an atomic scale
Hinkov and coworkers developed a new method and analysis software, and it provides answers. It is based on “resonant x-ray reflectometry”, a technique exploiting x-ray light created at a synchrotron, with the atomic-scale resolution of less than one nanometer. The physicists apply the technique on thin films of lanthanum cobalt oxide, a material that has interesting magnetic properties.
In their present work, however, the scientists have concentrated on another aspect: “Before we can delve in the rich magnetic phenomena of this material, we first have to solve a fundamental, very wide spread problem,” says Professor Hinkov. “Like many other materials, such as simple table salt and many semiconductors, lanthanum cobalt oxide consists of charged particles. These so-called ions form a sequence of positively and negatively charged atomic layers, stacked to a 15 nanometer thin film. “One can show that enormous electrostatic fields form between the layers, which is a problem, since they cost a lot of energy,” as Vladimir Hinkov explains.
“Nature is economical and avoids these field energy costs: It brings positive and negative charges to the opposite faces of the film, respectively, just like between the plates of a capacitor. A new field is formed, which is opposite to the original one and which cancels it.”
Corrugated interfaces constitute a problem
This accumulation of pure electronic charge at the film faces is called “electronic reconstruction”. According to the physicists, this is a very elegant solution, since it preserves the film face smoothness. For materials, in which electronic reconstruction is not possible, the compensating charge is provided by comparatively large ions, which results in corrugated film faces. As Hinkov explains, such corrugations are detrimental for devices based on film interfaces, especially when, like in transition-metal oxides, the material properties change on an atomic scale at the interface.
Exploiting the new method, the present work shows microscopic evidence that electronic reconstruction is indeed realized at transition-metal oxide interfaces. The method also provides a possibility to study the microscopic properties of such interfaces, which are not limited to electronic reconstruction, but encompass the arrangement of chemical elements, the electronic occupation of atomic orbitals and the spin orientation.
Successful by close, international collaboration
The special “Würzburg environment” and the close international collaboration enabled this successful work. “Such a scientific endeavor is only possible when experts from many different fields work closely together,” says Professor Hinkov. One needs excellent samples, high-precision x-ray scattering instruments, which are operated at modern synchrotron light sources, a dedicated software, and last but not least “colleagues who are willing to spend day and night at the synchrotron to perform the measurements.”
Valence-state reflectometry of complex oxide heterointerfaces. Jorge E Hamann-Borrero, Sebastian Macke, Woo Seok Choi, Ronny Sutarto, Feizhou He, Abdullah Radi, Ilya Elfimov, Robert J Green, Maurits W Haverkort, Volodymyr B Zabolotnyy, Ho Nyung Lee, George A Sawatzky & Vladimir Hinkov. doi:10.1038/npjquantmats.2016.13
Contact
Prof. Dr. Vladimir Hinkov, Lehrstuhl für Experimentelle Physik IV , T: (0931) 31-84481, hinkov@physik.uni-wuerzburg.de
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uni-wuerzburg.deAll latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Compact LCOS Microdisplay with Fast CMOS Backplane
…for High-Speed Light Modulation. Researchers from the Fraunhofer Institute for Photonic Microsystems IPMS, in collaboration with HOLOEYE Photonics AG, have developed a compact LCOS microdisplay with high refresh rates that…

New perspectives for material detection
CRC MARIE enters third funding period: A major success for terahertz research: Scientists at the University of Duisburg-Essen and the Ruhr University Bochum have been researching mobile material detection since…

CD Laboratory at TU Graz Researches New Semiconductor Materials
Using energy- and resource-saving methods, a research team at the Institute of Inorganic Chemistry at TU Graz aims to produce high-quality doped silicon layers for the electronics and solar industries….



