Discovery of high-speed moving plasma turbulence for the first time in the world
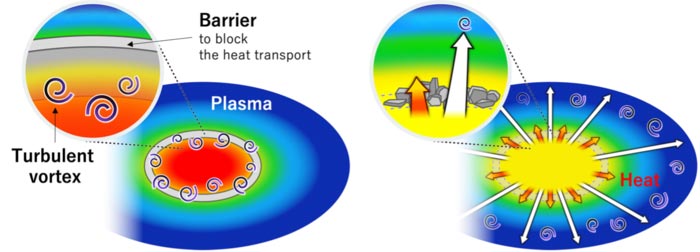
Fig.1 Left: Forming a barrier in the plasma to confirm heat inside. Right: By breaking the barrier, turbulence was discovered that moves faster than the heat, as the heat escapes from inside the plasma.
Credit: National Institute for Fusion Science
New insights into understanding turbulence in fusion plasmas.
Results shown in this article were published in a scientific journal of the Nature publishing group, Scientific Reports.
In order to achieve a fusion power plant, it is necessary to stably confine a plasma of more than 100 million degrees Celsius in a magnetic field and maintain it for a long time. A research group led by Assistant Professor Naoki Kenmochi, Professor Katsumi Ida, and Associate Professor Tokihiko Tokuzawa of the National Institute for Fusion Science (NIFS), National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NINS), Japan, using measuring instruments developed independently and with the cooperation of Professor Daniel J. den Hartog of the University of Wisconsin, USA, discovered for the first time in the world that turbulence moves faster than heat when heat escapes in plasmas in the Large Helical Device (LHD). One characteristic of this turbulence makes it possible to predict changes in plasma temperature, and it is expected that observation of turbulence will lead to the development of a method for real-time control of plasma temperature in the future.
In high-temperature plasma confined by the magnetic field, “turbulence,” which is a flow with vortexes of various sizes, is generated. This turbulence causes the plasma to be disturbed, and the heat from the confined plasma flows outward, resulting in a drop in plasma temperature. To solve this problem, it is necessary to understand the characteristics of heat and turbulence in plasma. However, the turbulence in plasmas is so complex that we have not yet achieved a full understanding of it. In particular, how the generated turbulence moves in the plasma is not well understood, because it requires instruments that can measure the time evolution of minute turbulence with high sensitivity and extremely high spaciotemporal resolution.
A “barrier” can form in the plasma, which acts to block the transport of heat from the center outward. The barrier makes a strong pressure gradient in the plasma and generates turbulence. Assistant Professor Kenmochi and his research group have developed a method to break this barrier by devising a magnetic field structure. This method allows us to focus on the heat and turbulence that flow vigorously as the barriers break, and to study their relationship in detail. Then, using electromagnetic waves of various wavelengths, we measured the changing temperature and heat flow of electrons and millimeter-sized fine turbulence with the world’s highest level of accuracy. Previously, heat and turbulence had been known to move almost simultaneously at a speed of 5,000 kilometers per hour, about the speed of an airplane, but this experiment led to the world’s first discovery of turbulence moving ahead of heat at a speed of 40,000 kilometers per hour. The speed of this turbulence is close to that of a rocket.
Assistant Professor Naoki Kenmochi said, “This research has dramatically advanced our understanding of turbulence in fusion plasmas. The new characteristic of turbulence, that it moves much faster than heat in a plasma, indicates that we may be able to predict plasma temperature changes by observing predictive turbulence. In the future, based on this, we expect to develop methods to control plasma temperatures in real-time.”
Journal: Scientific Reports
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-10499-z
Method of Research: Experimental study
Subject of Research: Not applicable
Article Title: Preceding propagation of turbulence pulses at avalanche events in a magnetically confined plasma
Article Publication Date: 16-May-2022
COI Statement: No conflict-of-interest statements.
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…


