Draw out of the predicted interatomic force
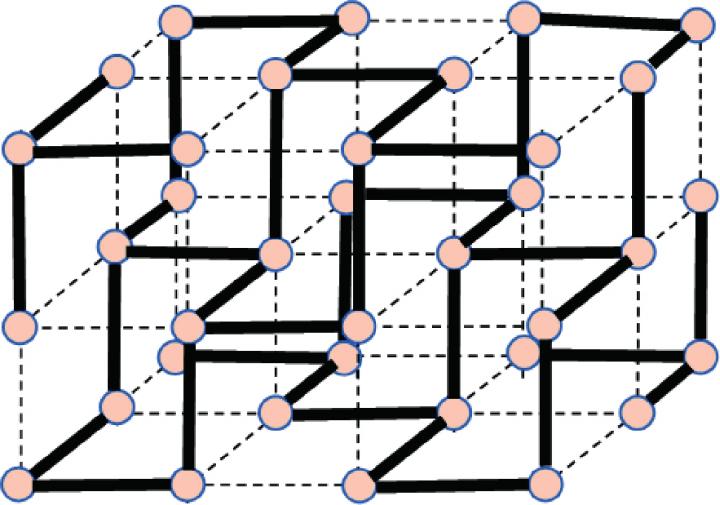
This is a schematic picture using simple cubic lattice, where bold and broken lines denote short strong bonds and long weak ones, respectively. Credit: M. Inui, Graduate School of Integrated Arts and Sciences, Hiroshima University, et al.
Liquid Bi shows a peculiar dispersion of the acoustic mode, which is related to the Peierls distortion in the crystalline state. These results will provide valuable inspiration to researchers developing new materials in the nanotechnology field.
Studies of the atomic dynamics in liquid Bi have been revisited more recently. The previous inelastic neutron scattering (INS) results for liquid Bi showed inconsistency for the inelastic excitation of the acoustic mode. These results were also different from the ab initio molecular dynamics (AIMD) prediction that indicated that the peculiar atomic dynamics arose from an anisotropic interatomic force in this monatomic liquid [1].
Therefore, it is important to observe the inelastic excitation of the acoustic mode in liquid Bi using inelastic x-ray scattering (IXS).
Professor M. Inui at Hiroshima University and his collaborators at Kumamoto University, Keio University, SPring-8/JASRI, and the RIKEN SPring-8 Center measured the IXS on liquid Bi at SPring-8 [2]. This research group found that the dispersion curve of the excitation energy of the acoustic mode exhibits a flat region as a function of the momentum transfer.
The experiments conducted by Professor Inui et al. used a single-crystal sapphire cell of the Tamura type that was carefully machined to provide a 0.04-mm sample thickness.
It is said that only his research group can make full use of this “world-famous” cell, which was used to stably conduct an x-ray beam experiment under high temperatures.
Furthermore, this research group reported that the IXS experimental results for liquid Bi clearly show a distinct inelastic excitation of the acoustic mode. This resolves the previous disagreement in the literature. Those researchers said, “Consistent with ab initio calculations of liquid Bi[1], the dispersion curve was nearly flat from 7 to 15 nm [to the negative 1 power].”
They also mentioned, “A long-range force is needed to reproduce the flatness of the dispersion curve, and the long-range force has to strongly be related to a local structure consisting of shorter and longer bounds in the liquid.”
This research group demonstrated a possible mechanism for the unusual dispersion of liquid Bi. Their results will greatly contribute to the development of nanotechnology.
###
Reference
[1] J. Souto et al., Phys. Rev. B 81, 134201 (2010)
[2] A.Q.R Baron et al., J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 61, 461 (2000).
Article information
[Journal]
Physical Review B
[Title]
Anomalous dispersion of the acoustic mode in liquid Bi
[Authors]
M. Inui, Y. Kajihara, S. Munejiri, S. Hosokawa, A. Chiba, K. Ohara, S. Tsutsui, and A. Q. R. Baron
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…


