Extending the power of attosecond spectroscopy
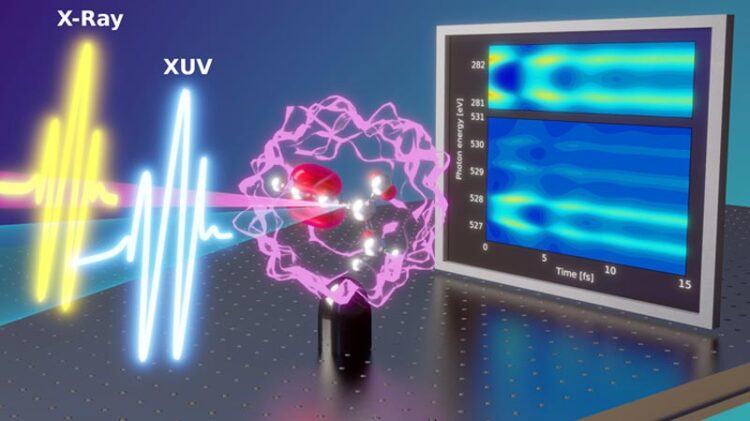
Fingerprints of ultrafast electron-nuclear dynamics obtained with attosecond transient absorption spectroscopy.
Credit: N. Golubev, EPFL
The last few decades have seen impressive progress in laser-based technologies, which have led to significant advancements in atomic and molecular physics. The development of ultrashort laser pulses now allows scientists to study extremely fast phenomena, like charge transport in molecules and elementary steps of chemical reactions. But beyond that, our ability to observe such processes on the attosecond scale (one quintillionth of a second) means that it is also possible to steer and probe the dynamics of individual electrons on their natural timeframes.
One of the emerging ultrafast technologies is attosecond transient absorption spectroscopy (ATAS), which can track the movement of electrons at a specific site of a molecule. This is a particularly appealing feature of ATAS, because it permits tracing the evolution of the molecular system with spatial resolution at the atomic scale.
Modern lasers can push chemistry into unexplored domains of light-matter interactions, where the role of theory in interpreting the results of ATAS measurements will be more important than ever before. But so far, the theory behind ATAS has been developed only for atoms or for molecules either in the absence of nuclear motion or in the absence of electronic coherence.
Now, a team of physicists from EPFL’s Laboratory of Theoretical Physical Chemistry (LCPT) have extended ATAS theory to molecules, including a full account of the correlated electron-nuclear dynamics.
The work, in collaboration with Alexander Kuleff at Heidelberg University, is published in Physical Review Letters.
“We present a simple quasi-analytical expression for the absorption cross-section of molecules, which accounts for the nuclear motion and non-adiabatic dynamics and is composed from physically intuitive terms,” says Nikolay Golubev, a postdoc at LCPT and the study’s lead author.
By extending ATAS theory, the scientists also show that this spectroscopy technique has sufficient resolution to “see” the follow-up decoherence of electron motion caused by the molecule’s nuclear rearrangement.
Putting theory into practice, the team tested the polyatomic molecule propiolic acid as an example. “The simulation of X-ray ATAS of the propiolic acid was made possible by combining high-level ab initio electronic structure methods with efficient semiclassical nuclear dynamics,” says Jiří Vaníček, head of the LCPT. By advancing our knowledge of the correlated motion of electrons and nuclei in molecules, the findings of the LCPT researchers could also help our understanding of various other “attochemistry” phenomena.
Reference
Nikolay V. Golubev, Jiří Vaníček, Alexander I. Kuleff. Core-valence attosecond transient absorption spectroscopy of polyatomic molecules. Physical Review Letters 127, 123001 (2021). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.127.123001
Journal: Physical Review Letters
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.127.123001
Method of Research: Computational simulation/modeling
Subject of Research: Not applicable
Article Title: Core-valence attosecond transient absorption spectroscopy of polyatomic molecules.
Article Publication Date: 16-Sep-2021
Media Contact
Nik Papageorgiou
Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne
n.papageorgiou@epfl.ch
Office: 41-216-932-105
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…


