Flow phenomena on solid surfaces: Physicists highlight key role played by boundary layer velocity
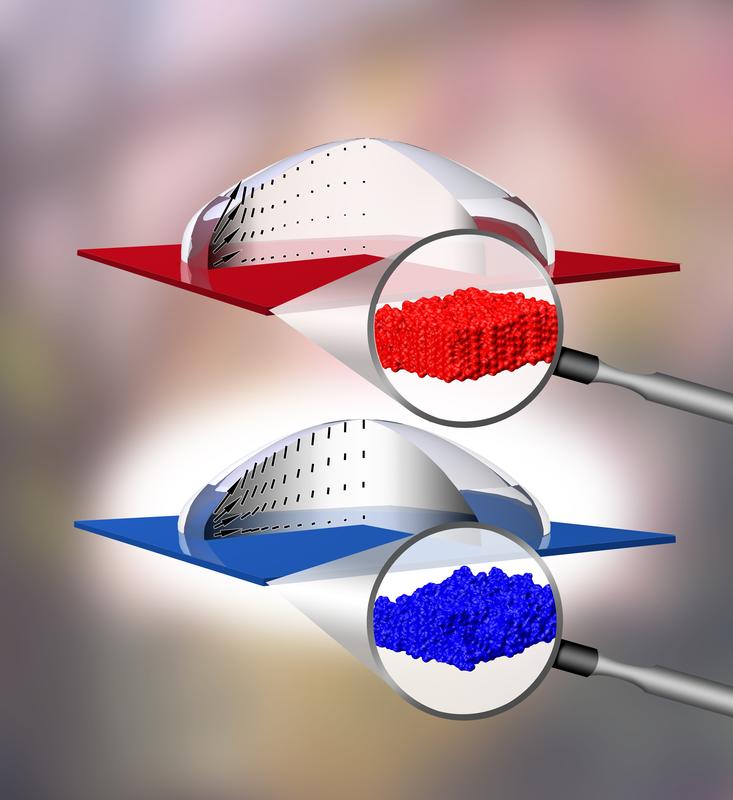
Polystyrene droplets on two different substrates slowly adopt the same equilibrium contact angle, but the velocity and flow profiles of the molecules in the droplets are different in the two cases. Illustration: Thomas Braun, Heidelberg
The study has been published in the respected academic journal PNAS (Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America).
When liquids flow over solid surfaces, their flow velocity in the immediate vicinity of the surface is zero. ‘By specially coating the surface, the boundary layer velocity can be increased. This also has the effect of reducing the shear forces within the liquid and of increasing its mean flow velocity. In the extreme case, the liquid behaves almost like a solid, but without exhibiting any change in its viscosity,’ explains Karin Jacobs, Professor of Experimental Physics at Saarland University.
Her research group has been conducting experiments on polystyrene droplets with the aim of uncovering the details of how different surfaces affect boundary layer velocities and the slip behaviour of liquid films. ‘Polystyrene is an important polymer that is used, for instance, to manufacture CD jewel cases,’ says Dr. Joshua D. McGraw.
The former postdoc in Jacobs’ research group headed the study, which was a collaborative effort with members of the research team led by Ralf Seemann, Professor of Experimental Physics at Saarland University, and researchers at ESPCI Paris Tech.
McGraw placed individual droplets of polystyrene (PS) onto thin mica substrates, where the droplets assumed a flattened form and sizes more than thousand times smaller than a typical rain drop. They were then frozen in this state and subsequently transferred onto two new ‘less PS-friendly’ substrates which differed from one another not in their chemical composition, but only in the spatial arrangement of their atoms.
On both substrates the droplets adopted an almost hemispherical form. ‘Droplets always show a tendency to adopt an equilibrium form in which they exhibit a definite contact angle to the surface. This equilibrium state is determined by the boundary layer conditions,’ explains Karin Jacobs.
Although the polystyrene droplets showed the same equilibrium contact angle on both substrates, droplet profile measurements made using an atomic force microscope indicated significant differences in the manner in which the droplets contracted, transforming from their original shape with the smaller contact angle to the new hemispherical form.
‘This can only mean that the molecules in the droplets move in two different ways on the two different surfaces, which in turn means that the velocity profiles in the two drops must be different,’ say Dr. Martin Brinkmann and Dr. Tak Shing Chan from Ralf Seemann’s group. ‘However, the required resolution is not available experimentally. That’s why we needed the support of the theoreticians in Paris.’
The researchers in Saarbrücken concluded that the velocity of the liquid at the solid surface is a key factor influencing the flow behaviour of such small droplets. The research colleagues at ESPCI Paris have managed to incorporate this into a theoretical model of the fluid dynamics. Martin Brinkmann and Tak Shing Chan were then able to use this theoretical description to conduct computer simulations that yield the molecular velocity field within a liquid drop.
‘This enabled us to demonstrate that even atomic-scale modifications to a solid surface can alter the speeds with which molecules move in liquid systems that are many orders of magnitude thicker than the surface coating itself,’ says Professor Jacobs, summarizing the results of the experiments.
The research results may help to optimize industrial processes, such as the extrusion of polymeric materials,’ says Karin Jacobs. Extrusion involves pressing a plastic through a forming die similar to the way that pasta dough is pushed through a pasta press when making fresh spaghetti or macaroni.
‘Once the dough has passed through the forming die, the strand expands as the material is now flowing more slowly,’ explains Jacobs. ‘This expansion of the material as it exits the die (known as “die swell”) is usually undesirable in industrial applications, but it may be possible to suppress die swell by suitably coating the inner surfaces of the die.’
Link to publication: http://www.pnas.org/content/early/2016/01/15/1513565113.abstract
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1513565113
Contact:
Prof. Dr. Karin Jacobs
Saarland University
Department of Experimental Physics
Tel.: +49 (0)681 302-71788
E-mail: k.jacobs@physik.uni-saarland.de
http://www.uni-saarland.de/jacobs
Dr. Joshua D. McGraw
Département de Physique
Ecole Normale Supérieure
Tel.: +33 1 44 32 35 50
Email: Joshua.mcgraw@phys.ens.fr
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…


