Giant leap for molecular measurements
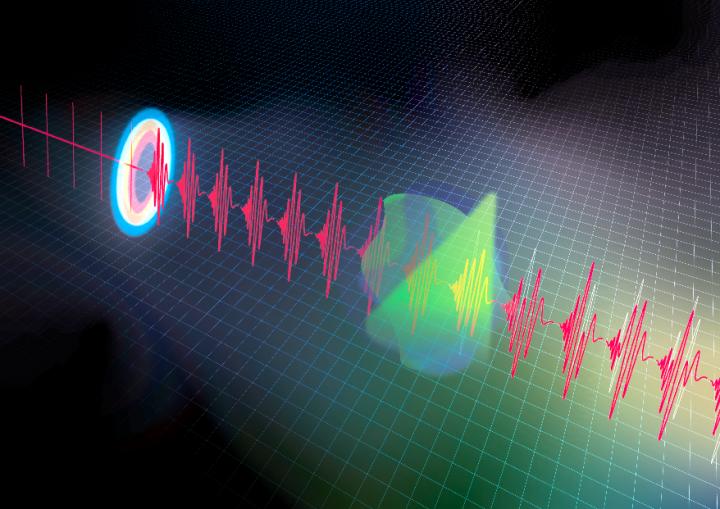
Laser pulses lasting for mere femtoseconds (one-quadrillionth of a second) are stretched to the nanosecond (one-billionth of a second) range.
Credit: © 2020 Ideguchi et al.
A new tool to analyze molecules is 100 times faster than previous methods
Spectroscopy is an important tool of observation in many areas of science and industry. Infrared spectroscopy is especially important in the world of chemistry where it is used to analyze and identify different molecules. The current state-of-the-art method can make approximately 1 million observations per second. UTokyo researchers have greatly surpassed this figure with a new method about 100 times faster.
From climate science to safety systems, manufacture to quality control of foodstuffs, infrared spectroscopy is used in so many academic and industrial fields that it’s a ubiquitous, albeit invisible, part of everyday life. In essence, infrared spectroscopy is a way to identify what molecules are present in a sample of a substance with a high degree of accuracy. The basic idea has been around for decades and has undergone improvements along the way.
In general, infrared spectroscopy works by measuring infrared light transmitted or reflected from molecules in a sample. The samples’ inherent vibrations alter the characteristics of the light in very specific ways, essentially providing a chemical fingerprint, or spectra, which is read by a detector and analyzer circuit or computer. Fifty years ago the best tools could measure one spectra per second, and for many applications this was more than adequate.
More recently, a technique called dual-comb spectroscopy achieved a measurement rate of 1 million spectra per second. However, in many instances, more rapid observations are required in order to produce fine-grain data. For example some researchers wish to explore the stages of certain chemical reactions that happen on very short time scales. This drive prompted Associate Professor Takuro Ideguchi from the Institute for Photon Science and Technology, at the University of Tokyo, and his team to look into and create the fastest infrared spectroscopy system to date.
“We developed the world’s fastest infrared spectrometer, which runs at 80 million spectra per second,” said Ideguchi. “This method, time-stretch infrared spectroscopy, is about 100 times faster than dual-comb spectroscopy, which had reached an upper speed limit due to issues of sensitivity.” Given there are around 30 million seconds in a year, this new method can achieve in one second what 50 years ago would have taken over two years.
Time-stretch infrared spectroscopy works by stretching a very short pulse of laser light transmitted from a sample. As the transmitted pulse is stretched, it becomes easier for a detector and accompanying electronic circuitry to accurately analyze. A key high-speed component that makes it possible is something called a quantum cascade detector, developed by one of the paper’s authors, Tatsuo Dougakiuchi from Hamamatsu Photonics.
“Natural science is based on experimental observations. Therefore, new measurement techniques can open up new scientific fields,” said Ideguchi. “Researchers in many fields can build on what we’ve done here and use our work to enhance their own understanding and powers of observation.”
###
Journal article
Akira Kawai, Kazuki Hashimoto, Tatsuo Dougakiuchi, Venkata Ramaiah Badarla, Takayuki Imamura, Tadataka Edamura and Takuro Ideguchi. Time-stretch infrared spectroscopy. Communications Physics. DOI: 10.1038/s42005-020-00420-3
Funding and support
This work was financially supported by JST PRESTO (JPMJPR17G2), JSPS KAKENHI (17H04852, 17K19071), Research Foundation for Opto-Science and Technology, and Murata Science Foundation.
Useful links
Ideguchi Group – https:/
Institute for Photon Science and Technology – http://www.
Graduate School of Science – https:/
Hamamatsu Photonics K.K. – https:/
Research Contact
Associate Professor Takuro Ideguchi
Institute for Photon Science and Technology, The University of Tokyo,
7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, 113-0033 Tokyo, Japan
Tel: +81-(0)3-5841-1026
Email: ideguchi@ipst.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp
Press Contact
Mr. Rohan Mehra
Division for Strategic Public Relations, The University of Tokyo
7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8654, JAPAN
Tel: +81-(0)80-9707-8450
Email: press-releases.adm@gs.mail.u-tokyo.ac.jp
About the University of Tokyo
The University of Tokyo is Japan’s leading university and one of the world’s top research universities. The vast research output of some 6,000 researchers is published in the world’s top journals across the arts and sciences. Our vibrant student body of around 15,000 undergraduate and 15,000 graduate students includes over 4,000 international students. Find out more at http://www.
Media Contact
Takuro Ideguchi
ideguchi@ipst.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp
81-035-841-1026
@UTokyo_News_en
Original Source
https://www.u-tokyo.ac.jp/focus/en/press/z0508_00128.html
Related Journal Article
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Parallel Paths: Understanding Malaria Resistance in Chimpanzees and Humans
The closest relatives of humans adapt genetically to habitats and infections Survival of the Fittest: Genetic Adaptations Uncovered in Chimpanzees Görlitz, 10.01.2025. Chimpanzees have genetic adaptations that help them survive…

You are What You Eat—Stanford Study Links Fiber to Anti-Cancer Gene Modulation
The Fiber Gap: A Growing Concern in American Diets Fiber is well known to be an important part of a healthy diet, yet less than 10% of Americans eat the minimum recommended…

Trust Your Gut—RNA-Protein Discovery for Better Immunity
HIRI researchers uncover control mechanisms of polysaccharide utilization in Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. Researchers at the Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based Infection Research (HIRI) and the Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) in Würzburg have identified a…



