GLOSTAR – tracing atomic and molecular gas in the Milky Way
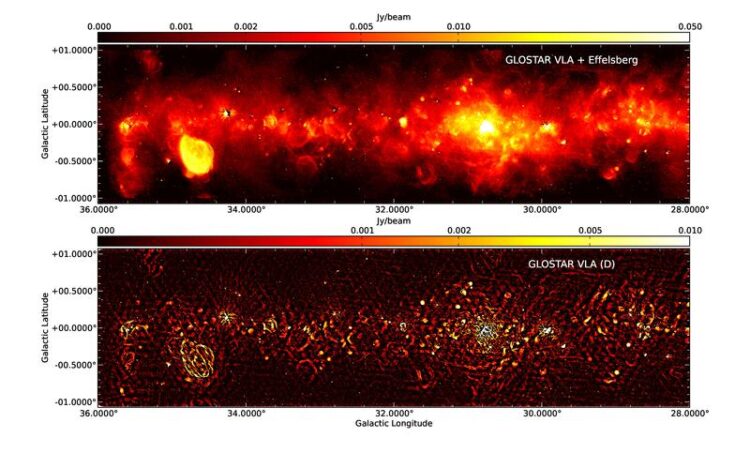
Top: Continuum radio image of the pilot region in the range 28° < l <36° from the combination of the VLA D-configuration and the Effelsberg single dish images. Bottom: VLA image of the same longitude range (see also Medina et al., 2019). (c) GLOSTAR Team
With two of the most powerful radio telescopes on Earth, an MPIfR-led team of researchers created the most sensitive maps of the radio emission of large parts of the Northern Galactic plane so far. The data were taken with the VLA (New Mexico) in two different configurations and the Effelsberg telescope. This is covering all angular scales down to 1.5 arc-seconds, the apparent size of a tennis ball on the ground seen from a flying plane. Contrary to previous surveys, GLOSTAR observed not only the radio continuum and polarization, but also spectral lines that trace the molecular gas (from methanol and formaldehyde) and atomic gas via radio recombination lines.

(c) Norbert Tacken/MPIfR (Effelsberg telescope); NRAO/AUI/NSF (Very Large Array)
The Global View on Star formation in the Milky Way (GLOSTAR) project provides the most sensitive maps of the radio emission of large parts of the Northern Galactic plane so far, taken with the Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) in New Mexico in two different configurations and MPIfR’s 100-m Effelsberg radio telescope. The exciting set of new data is now being used to study the interstellar medium in the Milky Way as well as massive stars in their infancy and their death. Shortly after the 50th birthday of the Effelsberg radio telescope, a series of papers based on the GLOSTAR data have now been published by Astronomy & Astrophysics.
While an interferometer like the VLA can produce very sharp images of the sky, the large-scale emission is often lost. However, the diffuse radio emission can be recovered by adding data from the 100-m Effelsberg telescope, as shown in Fig. 1. “This clearly demonstrates that the Effelberg telescope is still very crucial, even after 50 years of operation”, says Andreas Brunthaler, lead author of the first paper which gives an overview of the survey and describes the challenging data reduction techniques involved.
To map the full 145 square degrees of the survey, the team had to combine smaller images from almost 50,000 different positions. “We needed about 700 hours of observing time on the VLA, which generated almost 40 Terabyte in raw data”, explains Sergio Dzib, who led the data calibration efforts of the VLA data. While the Effelsberg part of the survey is ongoing, the survey data is already used for new and exciting science.
Previous surveys have detected only about 30% of the expected numbers of supernova remnants in the Milky Way. Thanks to the unprecedented sensitivity of the GLOSTAR survey, it was possible to find 80 new candidates in the VLA data alone, doubling the number in the observed area. With the addition of the Effelsberg data, this number is expected to rise. “This is an important step to solve this long-standing mystery of the missing supernova remnants”, explains Rohit Dokara, a doctoral student at the MPIfR and lead author on the second paper.
With the exciting results of the submm and far infrared wavelength surveys from the ground and space the massive and cold dust clumps from which massive clusters form are now detected galaxy wide. Complementary to these surveys, the GLOSTAR survey provides a very powerful and comprehensive images of, both, the ionized and molecular tracers of star formation in the Galactic plane.
The survey also covers the nearby Cygnus X star forming complex. Here, new sources with 6.7 GHz methanol maser emission were detected. “The 6.7 GHz line from methanol is exclusively found in regions where very massive stars of at least 8 Solar masses are formed”, says Karl Menten, director at the MPIfR, the initiator of GLOSTAR. He discovered this methanol maser, the second strongest radio wavelength spectral line, for the first time in the insterstellar medium exactly 30 years ago. While all methanol masers in the Cygnus X complex are associated with dust emission, less than half of the sources are also detected in the radio continuum.
“These masers are signposts for stars in a very early evolutionary stage, even before detectable radio emission can be seen”, explains Gisela Ortiz-León from the MPIfR, who leads the study of the Cygnus X region. Identifying genuine massive “proto”-stars has long been a goal of star formation research.
While optical light is heavily absorbed by interstellar dust, radio waves allow a peek into the most central regions of the Milky Way. Searching the new continuum map observed with the VLA towards the Galactic Center for radio emission associated with potential young stellar objects from a recently published catalogue, permits a better understanding of their evolutionary stage. “While we find radio emission for a good number of them, many of the objects lack radio counterparts and dust emission, suggesting that they are more evolved and have already dispersed their natal clouds”, reports Hans Nguyen, another doctoral student at the MPIfR, who is leading the study on these young stellar objects. The associated radio sources enable further constraints on the star formation rate in the Galactic Center.
To catalog the large number of sources is also challenging. The expected number of sources in the full GLOSTAR images is a few tens of thousands of sources of different nature. “There are nearly 100 sources per each square degree and we are using all available information to classify them”, explains Sac Medina, co-author of the four papers and a former PhD student at the MPIfR, who led the first source catalog paper and it is currently preparing the catalog of the full GLOSTAR D-configuration images.
Since its very early days, the MPIfR has conducted many extensive surveys of the radio sky, most of them at longer wavelengths. The GLOSTAR survey is the first survey in the 4-8 GHz regime that can rival with space IR surveys in terms of spatial scales and dynamical ranges and will therefore provide a unique data set with true legacy value for a global perspective on star formation in our Galaxy.
Background information:
GLOSTAR, the Global view on Star formation in the Milky Way survey uses the wideband (4-8 GHz) C-band receivers of the VLA and the Effelsberg 100-m radio telescope to conduct an unbiased survey to characterize star-forming regions in the Milky Way. This survey of the Galactic mid-plane detects tell-tale tracers of early phases of high-mass star formation: compact, ultra- and hyper-compact HII regions, and 6.7 GHz methanol (CH3OH) masers, which trace some of the earliest evolutionary stages in the formation of high-mass stars and can be used to pinpoint the positions of very young stellar objects, many of them still deeply embedded in their natal material. The observations center at 5.8 GHz and also cover emission from the 4.8 GHz formaldehyde (H2CO) and multiple Radio Recombination Lines (RRLs), all of which will be presented in future publications. The GLOSTAR observations were made with the VLA B- and D-configurations and the Effelsberg 100-m telescope for the large-scale structure.
MPIfR-based authors in the four GLOSTAR publications include (in alphabetical order): A. Brunthaler, C.-H. R. Chen, S. A. Dzib, R. Dokara, Y. Gong, C. König, S-N. X. Medina, K. M. Menten, P. Müller, H. Nguyen, G. N. Ortiz-León, W. Reich, M. R. Rugel, B. Winkel, A. Y. Yang and F. Wyrowski.
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Dr. Andreas Brunthaler
Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie, Bonn.
Fon: +49 228 525-377
E-Mail: brunthal@mpifr-bonn.mpg.de
Prof. Dr. Karl M. Menten
Director at MPIfR and Head of the “Millimeter and Submillimeter Astronomy” Research Dept.
Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie, Bonn.
Fon: +49 228 525-471 (secretary)
E-Mail: kmenten@mpifr-bonn.mpg.de
Dr. Sergio Dzib
Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie, Bonn.
Fon: +49 228 525-304
E-Mail: sdzib@mpifr-bonn.mpg.de
Originalpublikation:
A Global View on Star Formation: The GLOSTAR Galactic Plane Survey. I. – IV. (Brunthaler, A. et al.; Dokara, R. et al.; Ortiz-León, G.N. et al.; Nguyen, H. et al., 2021, Astronomy & Astrophysics (22. Juli 2021).
https://www.aanda.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202039856
https://www.aanda.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202039873
https://www.aanda.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202140817
https://www.aanda.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202140802
Weitere Informationen:
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…


