Heat transport through single molecules
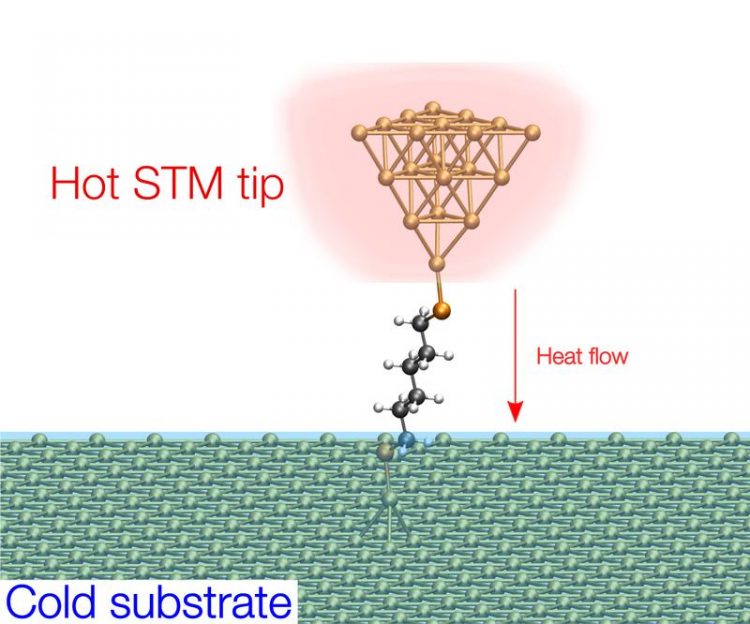
Illustration of the experimental setup to measure the heat flow through a single molecule. Copyright: Jan C. Klöckner
Combining novel theoretical and experimental approaches, researchers from the University of Michigan (USA), Kookmin University (South Korea), the University of Konstanz (Germany) and the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (Japan) have successfully measured and described the thermal conductance of single-molecule junctions – a key quantity in nanoscale transport phenomena that has so far eluded direct experimental determination. A joint paper entitled “Thermal Conductance of Single-Molecule Junctions” has been published online in the journal Nature on 17 July 2019.
“The control of heat transport at the molecular scale is a key factor in the development of nanostructured materials and technologies such as molecular electronics, thermally conductive polymers and thermoelectric energy-conversion devices”, explains Associate Professor Fabian Pauly, a theoretical condensed matter physicist and the leader of the Quantum Transport and Electronic Structure Theory Unit at Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University.
Fabian Pauly, who is also a Principal Investigator at the University of Konstanz’s Collaborative Research Centre 767 “Controlled Nanosystems: Interaction and Interfacing to the Macroscale”, contributed the theoretical models to the experimental breakthrough.
In short molecules, thermal energy transfer is believed to be determined by phase-coherent, ballistic processes as compared to incoherent and diffusive ones in conventional macroscopic systems.
“The problem is that while a range of other single-molecule-level transport properties have been successfully measured in the past, thermal conductance has proven difficult to determine due to considerable challenges associated with detecting extremely small heat currents at picowatt resolution”, Fabian Pauly continues.
Experimental breakthrough
Scientists from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at the University of Michigan managed to successfully measure thermal transport through single-molecule junctions for the very first time. They applied a custom-developed calorimetric-scanning-thermal-microscopy technique to prototypical thiol-terminated alkane molecules which were provided by researchers from the Department of Chemistry at Kookmin University in South Korea.
Working in an ultra-high vacuum environment, the US team used a self-assembled monolayer of alkane molecules to facilitate the formation of single-molecule junctions between a gold-coated microscope tip and a gold substrate.
The transfer of heat from the heated tip to the cold substrate, which was kept at room temperature throughout, allowed the researchers to determine the resulting thermal conductance, which was found to originate from the vibrations of atoms, also called phonons. A sophisticated averaging technique was required to measure the small quantity.
The theory behind the experiments
As Fabian Pauly points out: “Previous theoretical work conducted in my group made predictions on the size of thermal conductance values for various single-molecule junctions, providing important information to our experimental colleagues regarding the measurement resolution required to achieve successful quantification”.
Combining nonequilibrium Green’s function techniques with density functional theory in custom-developed code, Fabian Pauly and his doctoral student Jan Klöckner, who is based at University of Konstanz, were able to compute the thermal conductance due to phonons for junction geometries containing alkane molecules of variable length.
The experiments with such molecules that were conducted at the University of Michigan yield strong experimental evidence in support of the theorists’ assumptions of a phase-coherent transport regime. “In other words, heat transport in alkane-based single-molecule junctions is virtually independent of length”, explains Jan Klöckner, who helped to develop the ab initio simulations used to understand the experimental data.
These insights do not only resolve the longstanding problem of determining thermal conductance at the single-molecule level experimentally. They will also enable systematic studies of thermal transport through other one-dimensional systems such as polymer chains: “Having shown that heat transport at the molecular scale is length-independent, we must now try to find out how we can enhance or reduce it. Ultimately, what we hope to do in the future is to identify ways of controlling the flow of heat by molecular design”, concludes Fabian Pauly.
Facts:
– Original publication: Longji Cui, Sunghoon Hur, Zico Alaia Akbar, Jan C. Klöckner, Wonho Jeong, Fabian Pauly, Sung-Yeon Jang, Pramod Reddy, Edgar Meyhofer. Thermal Conductance of Single-Molecule Junctions. Nature, 17.07.2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1420-z.
– Researchers from the University of Michigan (USA), Kookmin University (South Korea), the University of Konstanz (Germany) and the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (Japan) have successfully measured and described the thermal conductance of single-molecule junctions for the first time
– Groundbreaking experiments, conducted at the University of Michigan, pave way for further research into thermal transport through single molecules and other one-dimensional systems
– Theoretical models developed by Fabian Pauly (University of Konstanz and Okinawa
Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University) and Jan Klöckner (University of Konstanz)
– Fabian Pauly’s and Jan Klöckner’s research supported by the University of Konstanz’s Collaborative Research Centre 767 “Controlled Nanosystems: Interaction and Interfacing to the Macroscale”
Note to editors:
An image is available for download here: https://cms.uni-konstanz.de/fileadmin/pi/fileserver/2019/Bilder/heat_transport_n…
Caption: Illustration of the experimental setup to measure the heat flow through a single molecule. A heated tip of a scanning tunneling microscope (STM) is brought close to a cold substrate so that a single molecule can bridge the gap between them.
Copyright: Jan C. Klöckner
Contact
University of Konstanz
Communications and Marketing
Phone: + 49 7531 88-3603
E-Mail: kum@uni-konstanz.de
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



