Hydrogen Bonds Directly Detected for the First Time
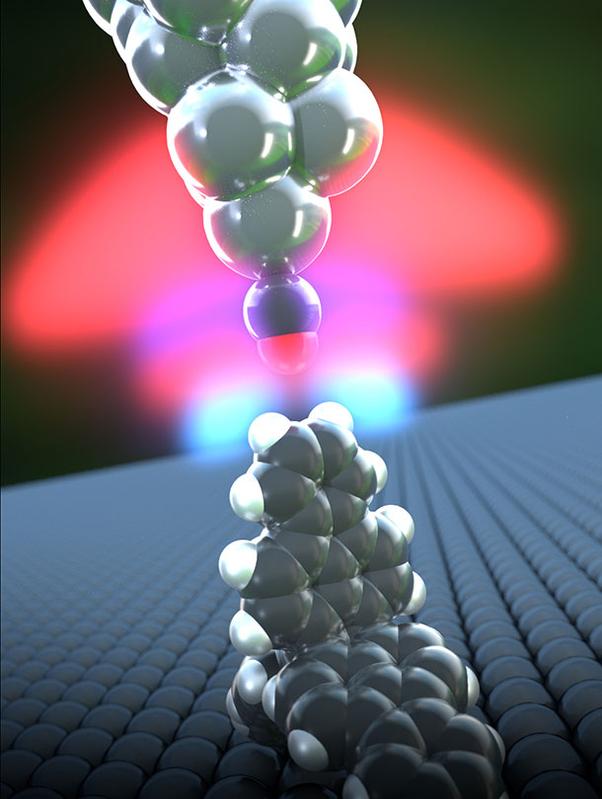
A hydrogen bond forms between a propellane (lower molecule) and the carbon monoxide functionalized tip of an atomic force microscope. University of Basel, Department of Physics
Hydrogen is the most common element in the universe and is an integral part of almost all organic compounds. Molecules and sections of macromolecules are connected to one another via hydrogen atoms, an interaction known as hydrogen bonding.
These interactions play an important role in nature, because they are responsible for specific properties of proteins or nucleic acids and, for example, also ensure that water has a high boiling temperature.
To date, it has not been possible to conduct a spectroscopic or electron microscopic analysis of hydrogen and the hydrogen bonds in single molecules, and investigations using atomic force microscopy have also not yielded any clear results.
Dr. Shigeki Kawai, from Professor Ernst Meyer’s team at the Swiss Nanoscience Institute and the Department of Physics at the University of Basel, has now succeeded in using a high-resolution atomic force microscope to study hydrogen atoms in individual cyclic hydrocarbon compounds.
Choosing the right molecules for a clear view
In close collaboration with colleagues from Japan, the researchers selected compounds whose configuration resembles that of a propeller. These propellanes arrange themselves on a surface in such a way that two hydrogen atoms always point upwards. If the tip of the atomic force microscope, which is functionalized with carbon monoxide, is brought close enough to these hydrogen atoms, hydrogen bonds are formed that can then be examined.
Hydrogen bonds are much weaker than chemical bonds, but stronger than intermolecular van der Waals interactions. The measured forces and distances between the oxygen atoms at the tip of the atomic force microscope and the propellane’s hydrogen atoms correspond very well to the calculations performed by Prof. Adam S. Foster from Aalto University in Finland. They show that the interaction clearly involves hydrogen bonds. The measurements mean that the much weaker van der Waals forces and the stronger ionic bonds can be excluded.
With this study, the researchers from the University of Basel’s Swiss Nanoscience Institute network have opened up new ways to identify three-dimensional molecules such as nucleic acids or polymers via observation of hydrogen atoms.
Original source
Shigeki Kawai, Tomohiko Nishiuchi, Takuya Kodama, Peter Spijker, Rémy Pawlak, Tobias Meier, John Tracey, Takashi Kubo, Ernst Meyer, Adam S. Foster
Direct quantitative measurement of the C=O···H-C bond by atomic force microscopy
Science Advances (2017), doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1603258
Further information
Prof. Dr. Ernst Meyer, University of Basel, Department of Physics, tel. +41 61 207 37 24, email: ernst.meyer@unibas.ch
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.unibas.chAll latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…


