Laser-controlled novel superconductors could pave the way to future quantum computers
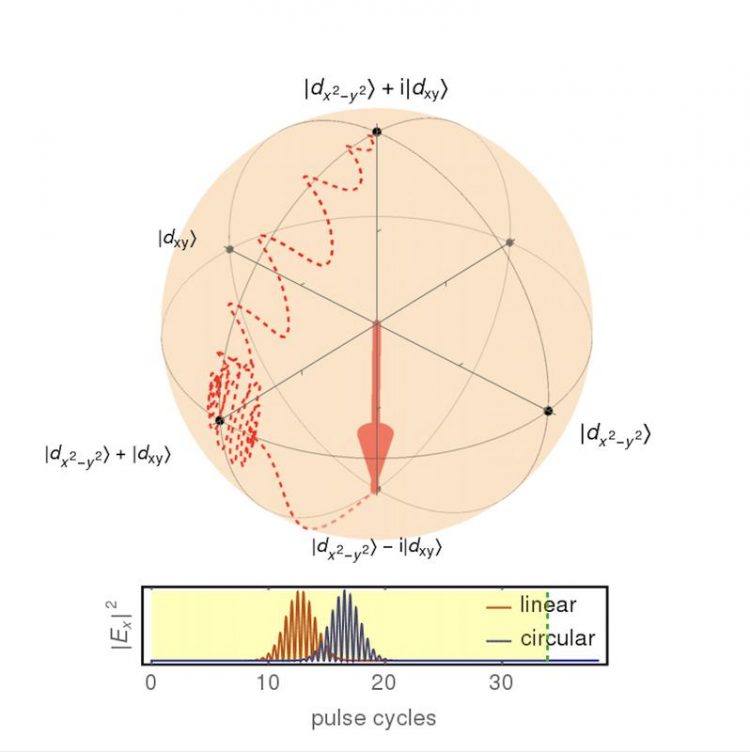
Switching of a two-component chiral order parameter represented on the Bloch sphere Martin Claassen / Nature Physics
The use of strong electromagnetic radiation to push materials out of their normal equilibrium is a new frontier in this field. Such manipulation leads to the emergence of new phases with novel, useful and controllable properties.
Now, a team of scientists in the USA and Germany has shown that tailored laser pulses can be used to control the properties of chiral topological superconductors. Their work has just been published in Nature Physics.
Superconductors are materials which can conduct electricity without resistance. Currently, this only happens in specific circumstances, for example at very low temperatures. Chiral topological superconductors are a particular class which hosts an elusive particle called a Majorana fermion.
This can be used to encode quantum bits and perform error-resilient computation. However, controlling and manipulating these emergent properties poses a significant challenge.
Fundamentally, the chiral topological nature of these materials relies on the rotation and reflection symmetries of the crystal lattice to maintain a subtle balance between competing superconducting states. The researchers from the Flatiron Institute’s Center for Computational Quantum Physics (CCQ) in New York City (USA), Freie Universität Berlin and the Max Planck Institute for the Structure and Dynamics of Matter (both in Germany) found that a weak pulse can disrupt this balance and induce a dramatic change in the underlying electronic order. This occurs because the pulse selectively breaks these symmetries via choice of polarization.
In particular, the team showed numerically that an appropriately-tuned pulse sequence can selectively reverse the “handedness” of a chirally-superconducting region on a very fast time scale (on the order of picoseconds – a trillionth of a second). This handedness is an intrinsic topological property of such materials and sets the propagation direction (clockwise or counter-clockwise) of Majorana fermions that are induced along its boundary.
An intriguing consequence of their work is the possibility to optically “program” topologically-protected quantum circuits, to perform computation on the charging states of single electrons injected into the Majorana boundary modes. Furthermore, the underlying mechanism is robust and relies solely on symmetry, not on the materials’ details. It could be applied to any material with multi-component order parameters.
The scientists predict that topological superconductivity can be detected in time-resolved pump-probe experiments where an initial laser pulse alters the superconducting state in the material and a second ‘reads’ these changes after a short delay. This establishes pump-probe experiments as a new experimental tool to reveal the putative chiral topological nature of superconductivity in a wide array of candidate materials such as Sr2RuO4, twisted bilayer graphene, SrPtAs, or UPt3.
Martin Claassen, PhD
Flatiron Research Fellow
Simons Foundation, Flatiron Institute
Center for Computational Quantum Physics
162 Fifth Avenue
New York, United States
Universal optical control of chiral superconductors and Majorana modes
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

New Study Offers Hope for Chronic Pain Relief in Dialysis Patients
People undergoing hemodialysis treatment for kidney failure often experience chronic pain related to their condition, but it can be difficult to manage with opioid medication and other conventional treatments. A…

Early Adult Mortality Surges in Post-COVID US
New research from Boston University School of Public Health and the University of Minnesota shows that death rates for early adults, or adults aged 25-44, rose sharply during the COVID-19…

Recycling Lithium-Ion Batteries Boosts Supply Chain Resilience
Recycling lithium-ion batteries to recover their critical metals has significantly lower environmental impacts than mining virgin metals, according to a new Stanford University lifecycle analysis published in Nature Communications. On…



