Long-term liquid water also on non-Earth-like planets?
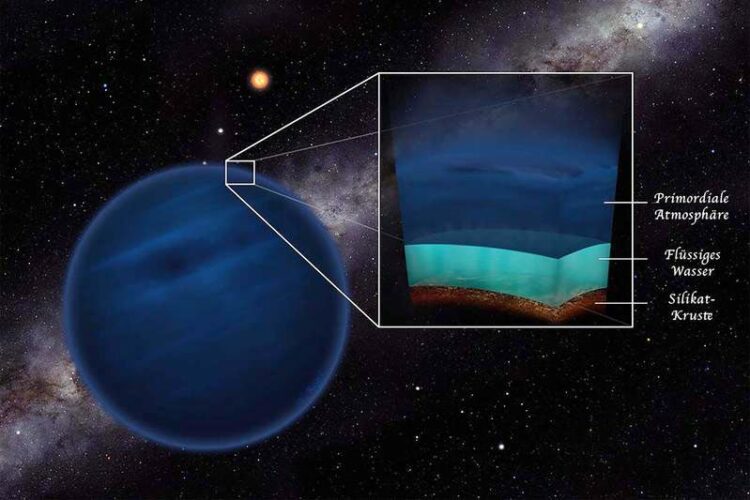
Low-mass planets with a primordial atmosphere of hydrogen and helium might have the temperatures and pressures that allow water in the liquid phase. The presence of liquid water is favorable for life, so that these planets potentially harbour exotic habitats for billions of years.
Credit: © (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) - Thibaut Roger - Universität Bern - Universität Zürich
Liquid water is an important prerequisite for life to develop on a planet. As researchers from the University of Bern, the University of Zurich and the National Centre of Competence in Research (NCCR) PlanetS report in a new study, liquid water could also exist for billions of years on planets that are very different from Earth. This calls our currently Earth-centred idea of potentially habitable planets into question.
Life on Earth began in the oceans. In the search for life on other planets, the potential for liquid water is therefore a key ingredient. To find it, scientists have traditionally looked for planets similar to our own. Yet, long-term liquid water does not necessarily have to occur under similar circumstances as on Earth. Researchers of the University of Bern and the University of Zurich, who are members of the National Centre of Competence in Research (NCCR) PlanetS, report in a study published in the journal Nature Astronomy, that favourable conditions might even occur for billions of years on planets that barely resemble our home planet at all.
Primordial greenhouses
“One of the reasons that water can be liquid on Earth is its atmosphere”, study co-author Ravit Helled, Professor of Theoretical Astrophysics at the University of Zurich and a member of the NCCR PlanetS explains. “With its natural greenhouse effect, it traps just the right amount of heat to create the right conditions for oceans, rivers and rain”, says the researcher.
Earth’s atmosphere used to be very different in its ancient history, however. “When the planet first formed out of cosmic gas and dust, it collected an atmosphere consisting mostly of Hydrogen and Helium – a so-called primordial atmosphere”, Helled points out. Over the course of its development, however, Earth lost this primordial atmosphere.
Other, more massive planets can collect much larger primordial atmospheres, which they can keep indefinitely in some cases. “Such massive primordial atmospheres can also induce a greenhouse effect – much like Earth’s atmosphere today. We therefore wanted to find out if these atmospheres can help to create the necessary conditions for liquid water”, Helled says.
Liquid water for billions of years
To do so, the team thoroughly modelled countless planets and simulated their development over billions of years. They accounted not only for properties of the planets’ atmospheres but also the intensity of the radiation of their respective stars as well as the planets’ internal heat radiating outwards. While on Earth, this geothermal heat plays only a minor role for the conditions on the surface, it can contribute more significantly on planets with massive primordial atmospheres.
“What we found is that in many cases, primordial atmospheres were lost due to intense radiation from stars, especially on planets that are close to their star. But in the cases where the atmospheres remain, the right conditions for liquid water can occur”, reports Marit Mol Lous, PhD student and lead-author of the study. According to the researcher at the University of Bern and the University of Zurich, “in cases where sufficient geothermal heat reaches the surface, radiation from a star like the Sun is not even necessary so that conditions prevail at the surface that allow the existence of liquid water.”
“Perhaps most importantly, our results show that these conditions can persist for very long periods of time – up to tens of billions of years”, points out the researcher, who is also a member of the NCCR PlanetS.
Broadening the horizon for the search for extraterrestrial life
“To many, this may come as a surprise. Astronomers typically expect liquid water to occur in regions around stars that receive just the right amount of radiation: not too much, so that the water does not evaporate, and not too little, so that it does not all freeze”, study co-author Christoph Mordasini, Professor of Theoretical Astrophysics at the University of Bern and member of the NCCR PlanetS explains.
“Since the availability of liquid water is a likely prerequisite for life, and life probably took many millions of years to emerge on Earth, this could greatly expand the horizon for the search for alien lifeforms. Based on our results, it could even emerge on so-called free-floating planets, that do not orbit around a star”, Mordasini says.
Yet the researcher remains cautious: “While our results are exciting, they should be considered with a grain of salt. For such planets to have liquid water for a long time, they have to have the right amount of atmosphere. We do not know how common that is.”
“And even under the right conditions, it is unclear how likely it is for life to emerge in such an exotic potential habitat. That is a question for astrobiologists. Still, with our work we showed that our Earth-centred idea of a life-friendly planet might be too narrow”, Mordasini concludes.
Bernese space exploration: With the world’s elite since the first moon landing
When the second man, “Buzz” Aldrin, stepped out of the lunar module on July 21, 1969, the first task he did was to set up the Bernese Solar Wind Composition experiment (SWC) also known as the “solar wind sail” by planting it in the ground of the moon, even before the American flag. This experiment, which was planned, built and the results analysed by Prof. Dr. Johannes Geiss and his team from the Physics Institute of the University of Bern, was the first great highlight in the history of Bernese space exploration.
Ever since Bernese space exploration has been among the world’s elite, and the University of Bern has been participating in space missions of the major space organizations, such as ESA, NASA, and JAXA. With CHEOPS the University of Bern shares responsibility with ESA for a whole mission. In addition, Bernese researchers are among the world leaders when it comes to models and simulations of the formation and development of planets.
The successful work of the Department of Space Research and Planetary Sciences (WP) from the Physics Institute of the University of Bern was consolidated by the foundation of a university competence center, the Center for Space and Habitability (CSH). The Swiss National Fund also awarded the University of Bern the National Center of Competence in Research (NCCR) PlanetS, which it manages together with the University of Geneva.
UZH Space Hub
Founded in 2018 UZH Space Hub – the space and aviation cluster of UZH innovation hub – is now one of the globally significant space hubs. With its 35 high ranked research groups from the fields of earth observation, space life sciences, astrophysics and supercomputing, autonomous flying and navigation of unmanned aerial vehicles, green aviation and space sustainability UZH Space Hub is perfectly positioned to play a decisive role in the shaping of the growing space economy and space industry. More information
Journal: Nature Astronomy
DOI: 10.1038/s41550-022-01699-8
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…


