Mysteries in clouds
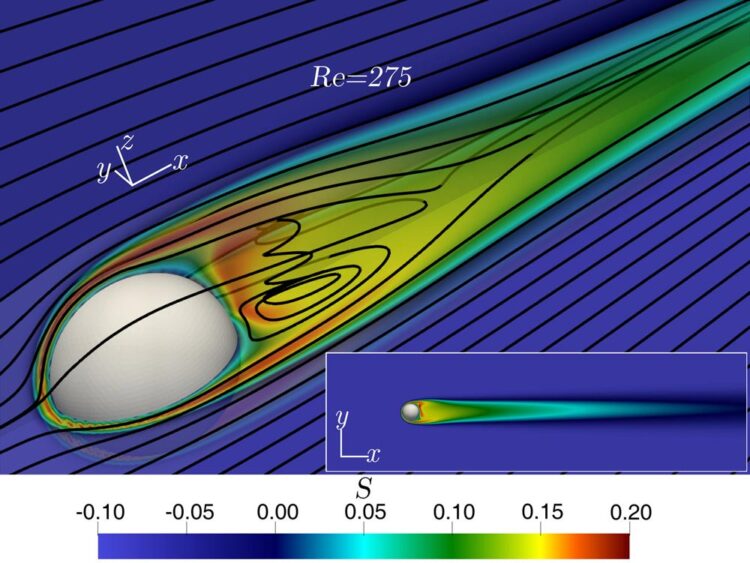
Überschüssiger Wasserdampf (S>0) hinter einem ausfallenden gefrorenen Hydrometeor bei 0°C Temperatur, der durch eine Umgebung bei -15°C und 90% relativer Feuchte fällt. In der schwarzen Linie ist ein Aerosol zu sehen, das in die wasserdampfreiche Umgebung eintritt.
© MPIDS
Large droplets favoring creation of smaller ones
Scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Dynamics and Self-Organization (MPIDS) reported their new findings on how precipitating large raindrops, ice particles can favor growth of aerosols to produce new cloud condensation nuclei or ice nucleating particles. The results were recently published in the Geophysical Research Letters.
Atmospheric clouds play a crucial role in defining the local weather and global climate. When cloud aerosols grow to a certain size by collecting water, scientists call it activation. The activation of cloud aerosols, such as mineral dust, soot particles, pollutants, acid molecules and ions, impacts the life cycle of a cloud. Therefore, a detailed understanding is necessary for reliable climate prediction and weather forecasting. Out of many mysteries of clouds, we still do not understand how and why the number of ice particles inside clouds exceed the number of ice nucleating particles that could be activated. What are the major sources behind this excess (secondary) production of particles?
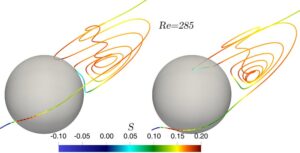
© MPIDS
In their recent publication, the scientists of MPIDS have numerically investigated one such secondary particle production processes inside clouds resulting to new water droplets or ice particles. Out of several proposed physical processes for new droplet generation, recent experimental studies have shown that a large droplet can nucleate aerosols, i.e. it generates small water particles out of aerosols in the wake behind it when falling under gravity. Extending the experiments, this letter presents a detailed analysis of various physical factors that lead to an excess of water vapor condition behind the hydrometeors (e.g., droplets, sleet, or hail) and investigates the effectiveness of this process on activation of aerosols to create new cloud particles.
“Not all aerosols, but only some ‘lucky aerosols’ are entrained in the wake behind such precipitating hydrometeors, where they can reside in a highly humid environment for sufficiently long time. This fulfills the necessary condition for the aerosols to be activated as new cloud condensation nuclei or ice nucleating particles by deposition of water vapor”, explained Taraprasad Bhowmick, first author of the article. This work also reports how this activation of aerosols by hydrometeors can contribute to the life cycle of the clouds.
“This study opened new potential research areas. Our group of scientists from MPIDS are looking forward to extend this work with more realistic modeling of the cloud conditions, and plan to carry out a detailed growth tracking of individual aerosols that come in contact with such precipitating cloud hydrometeors”, says Prof. Eberhard Bodenschatz, leader of the working group.
This research was supported by the Marie‐Skłodowska Curie Actions (MSCA) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (Grant Agreement No. 675675), and an extension to program COMPLETE by Department of Applied Science and Technology, Politecnico di Torino, Italy.
Originalpublikation:
Bhowmick, T., Wang, Y., Iovieno, M., Bagheri, G., & Bodenschatz, E.
Supersaturation in the wake of a precipitating hydrometeor and its impact on aerosol activation
Geophysical Research Letters 47 (22) (2020) e2020GL091179
DOI: 10.1029/2020GL091179
https://www.ds.mpg.de/3687170/201218_cloud_mysteries
Contact
MPIDS press office
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…


