New 2D-based photodetector developed with fast and broadband photoresponse
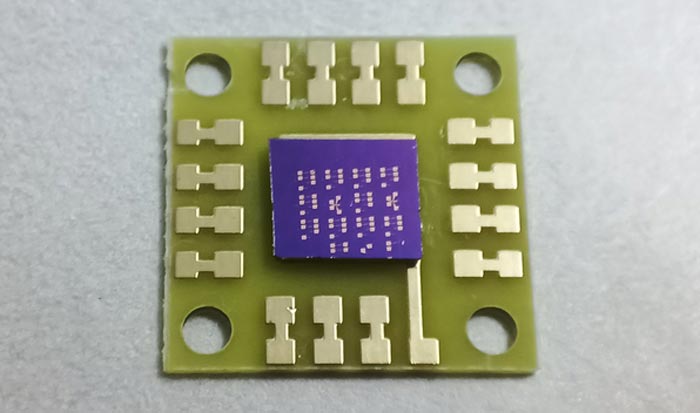
Prototype device for point photodetection base on 2D InSiTe3
Credit: LI Liang
Recently, a collaborated team led by Prof. LI Liang and Prof. LI Guanghai at the Institute of Solid State Physics (ISSP), Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), together with Prof. YAN Feng from Hong Kong Polytechnic University (PolyU) developed a new 2D-based photodetector, featuring on ultrafast photoresponse and broadband detection capabilities.
The photodetector, which was introduced in a paper recently published in ACS Nano, was made from layered ternary telluride InSiTe3.
Photodetectors with broadband detection capabilities play a crucial role in our daily lives and have been extensively used in a wide range of applications. Many 2D materials-based photodetectors exhibit high photoresponsivity and detectivity but slow response speed, which can be attributed to their prolonged excess carrier lifetime. Such slow speed performance has become a bottleneck for 2D materials-based photodetectors in practical applications, especially optical communication.
“We found the response of this InSiTe3-based photodetector stable and reversible.” said Prof. LI Liang.
In their experiment, the photos responded within 545–576 ns, and the detection capabilities from the ultraviolet (UV) to the near-infrared (NIR) optical communication region ranged from 365–1310 nm.
The promising photodetector is based on ternary telluride InSiTe3 with trigonal symmetry and a layered structure. Scientists synthesized high-quality InSiTe3 crystals and determined its Raman vibration modes by Raman spectra measurements.
They found that the indirect band gap of InSiTe3 can be tuned from 1.30 eV (monolayer) to 0.78 eV (bulk). Moreover, the InSiTe3-based photodetectors exhibit the detectivity of 7.59 × 109 Jones.
These outstanding performance values highlight the potential of 2D InSiTe3-based photodetectors in high-speed broadband photodetection.
Journal: ACS Nano
DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.1c11628
Article Title: A Submicrosecond-Response Ultraviolet–Visible–Near-Infrared Broadband Photodetector Based on 2D Tellurosilicate InSiTe3
Article Publication Date: 2-May-2022
Media Contact
Weiwei Zhao
Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences
annyzhao@ipp.ac.cn
Office: 86-551-655-91206
Original Source
https://english.hf.cas.cn/nr/rn/202205/t20220507_305092.html
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…


