Optical bimeron: A new topological state of light
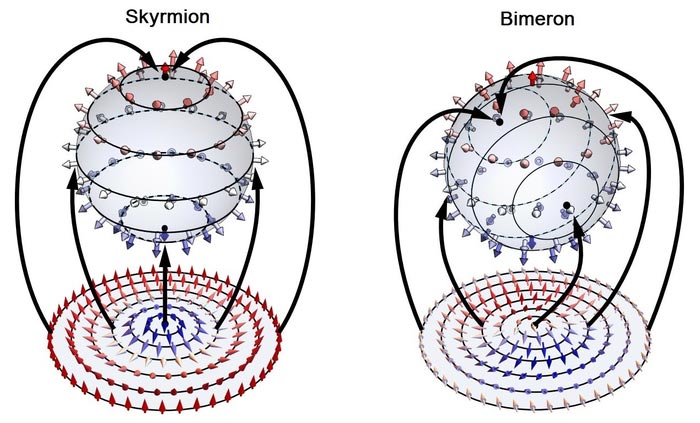
Skyrmion can be represented as a set of 3D vectors confined in 2D plane unwrapped from a unit spiny sphere. Bimeron, a topological transition state of skyrmion, can also be described by the unit sphere mapping, but by changing a wrapping style for the fixed spiny sphere but the coordinates of longitude and latitude are switched, or tuning the longitude and latitude coordinates with a fixed spiny sphere.
Credit by Yijie Shen / License CC BY
Topological quasiparticles with sophisticated spin textures are intriguing objects in particle physics and magnetic materials that exhibit exotic physics and have potential applications in information storage and processing. The most fundamental and exemplary topological spin texture is called the skyrmion, which is a nanoscale circular domain wall carrying a nonzero integer topological charge.
The skyrmion texture was recently realized in structured optical fields, as a powerful tool to open new research directions of topological photonics. Since the first observation of optical skyrmions, the researchers have focused on the exploration of more general topological spin textures evolved from the skyrmion.
In a recent theoretical work carried out by a research fellow in University of Southampton, Dr. Yijie Shen, a new type of topological quasiparticle state in optical field beyond the limit of skyrmion, which is called the optical bimeron. Bimeron is a topological counterpart of skyrmion and can be seen as a combination of two half-skyrmions (merons) with opposite polarities.
The importance of bimerons has been well endorsed in fundamental particles and magnetic materials, because it possesses more general topological states than conventional skyrmion, but it was never studied in optical fields. Dr. Shen’s paper fills the gap, which has been published online on 29 July in the journal Optics Letters (https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.431122). This article has been highlighted as an Editor’s Pick.
The method to realize optical bimeron is to tailor a special family of structured vector beam in which the polarization Stokes vectors can construct devise textures akin to bimerons. Tailoring light is much like tailoring cloth, cutting and snipping to turn a bland fabric into one with some desired pattern. In the case of light, the tailoring is usually done in the spatial degrees of freedom, such as its amplitude and phase (the “pattern” of light), and its polarization, while the cutting and snipping might be control with spatial light modulators and the like. For optical bimeron, we just need to tailor a bimeronic cloth for structured light.
“The meaning of bimeronic beams is towards the general control of topological light, which can be transformed to diverse generalized topological textures, including all the intermediate skyrmionic states among Néel-, Bloch-, and anti-skyrmion types as simple members.” says Dr. Shen. Moreover, in the paper, a graphical model is proposed to universally represent such general topological evolution of tunable bimeronic beams onto a 3D Poincaré-like sphere, as a vivid graphical toolkit to guide future applications.
As a remarkable merit of optical bimeron, it can propagate in free space with salient topology-dependent dynamics. A bimerionic beam, constructed by a fundamental and vortex spatial modes with different polarizations, will undergo a propagation-dependent dynamic phase difference between the two polarized components, which induces the longitudinal-variant vector patterns. Therefore, you can theoretically see multiple topological states in different transverse planes along the light propagation direction. Also, such 3D vector patterns of bimerionic beams with elegant topological characterization meet the urgently demanded techniques for higher-dimensional structured light control, which promises the applications of modern optical communications and encryption with increasing demands of large capacity and high speed in information encoding.
Media Contact
Yaobiao Li
liyaobiao@ciomp.ac.cn
Office: 86-431-861-76851
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Pinpointing hydrogen isotopes in titanium hydride nanofilms
Although it is the smallest and lightest atom, hydrogen can have a big impact by infiltrating other materials and affecting their properties, such as superconductivity and metal-insulator-transitions. Now, researchers from…

A new way of entangling light and sound
For a wide variety of emerging quantum technologies, such as secure quantum communications and quantum computing, quantum entanglement is a prerequisite. Scientists at the Max-Planck-Institute for the Science of Light…

Telescope for NASA’s Roman Mission complete, delivered to Goddard
NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope is one giant step closer to unlocking the mysteries of the universe. The mission has now received its final major delivery: the Optical Telescope…



