'Optical rocket' created with intense laser light
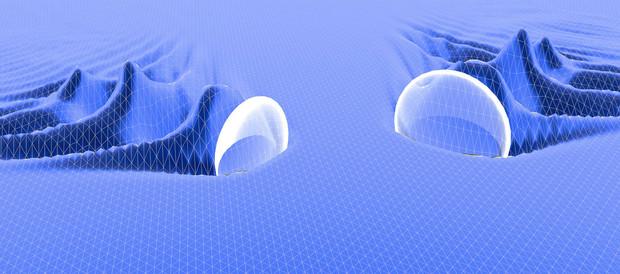
In this artist's conception of the Nebraska experiment, the white orbs represent two laser pulses, with plasma waves in their wakes. The waves interfere with one another after the laser pulses cross, and electrons ride the wakefield waves to higher energy. Credit: Extreme Light Laboratory, University of Nebraska-Lincoln
In a recent experiment at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln, plasma electrons in the paths of intense laser light pulses were almost instantly accelerated close to the speed of light.
Physics professor Donald Umstadter, who led the research, said the new application might aptly be called an “optical rocket” because of the tremendous amount of force that light exerted in the experiment. The electrons were subjected to a force almost a trillion-trillion-times greater than that felt by an astronaut launched into space.
“This new and unique application of intense light can improve the performance of compact electron accelerators,” he said. “But the novel and more general scientific aspect of our results is that the application of force of light resulted in the direct acceleration of matter.”
The optical rocket is the latest example of how the forces exerted by light can be used as tools, Umstadter said.
Normal intensity light exerts a tiny force whenever it reflects, scatters or is absorbed. One proposed application of this force is a “light sail” that could be used to propel spacecraft. Yet because the light force is exceedingly small in this case, it would need to be exerted continuously for years for the spacecraft to reach high speed.
Another type of force arises when light has an intensity gradient. One application of this light force is an “optical tweezer” that is used to manipulate microscopic objects. Here again, the force is exceedingly small.
In the Nebraska experiment, the laser pulses were focused in plasma. When electrons in the plasma were expelled from the paths of the light pulses by their gradient forces, plasma waves were driven in the wakes of the pulses, and electrons were allowed to catch the wakefield waves, which further accelerated the electrons to ultra-relativistic energy. The new application of intense light provides a means to control the initial phase of wakefield acceleration and improve the performance of a new generation of compact electron accelerators, which are expected to pave the way for a range of applications that were previously impractical because of the enormous size of conventional accelerators.
###
The experimental research was conducted by students and scientists at Nebraska, with senior research associate Grigoroy Golovin serving as lead author on the paper reporting the new result. Funding was provided by the National Science Foundation.
The experiment was based upon numerical modeling by scientists from Shanghai Jiao Tong University in China. Umstadter theoretically predicted the underlying mechanism two decades ago. The results were reported in September in the journal Physical Review Letters.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…


