This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
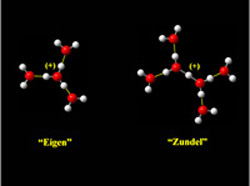
Free protons from acids associate with 1, 2 or 3 molecules of water and the structures can be identified by unique infrared laser spectrum signatures, according to a report in Science by Yale professor of chemistry Mark A. Johnson and his collaborators at Yale, the University of Pittsburgh and the University of Georgia.
Acids yielding free protons are common in biological and chemical systems and the measurement of pH to determine acidity of an aqueous solution is a simple, stand

Astronomers Having Used ESO Telescopes Start Analysing Unique Dataset on the Comet Following the Deep Impact Mission
Ten days after part of the Deep Impact spacecraft plunged onto Comet Tempel 1 with the aim to create a crater and expose pristine material from beneath the surface, astronomers are back in the ESO Offices in Santiago, after more than a week of observing at the ESO La Silla Paranal Observatory. In this unprecedented observing campaign – among the most ambitious ever

A gigantic explosion on a neutron star halfway across the Milky Way galaxy, the largest such explosion ever recorded in the universe, should allow astronomers for the first time to probe the interiors of these mysterious stellar objects.
An international team of astrophysicists, combing through data from a NASA X-ray satellite, the Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer, reports in the July 20th issue of Astrophysical Journal Letters that the explosion produced vibrations within the star,

A team of scientists at the Weizmann Institute of Science has recently demonstrated conclusively that, in very specific circumstances, spin can become separated from charge and progress independently down a wire
Two properties of an electron – its spin and its charge – are generally thought to be inseparable, intrinsic characteristics, no more given to sudden changes or going off on their own than say, the fur on a cat or the paint on a bicycle. But a team of scientists at the W

Using a technique called ultrasonic spray pyrolysis, researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have created an improved catalyst for removing smelly sulfur-containing compounds from gasoline and other fossil fuels. The improved catalyst is a form of molybdenum disulfide, most commonly recognized as the black lubricant used to grease automobiles and machinery.
Molybdenum disulfide is made of long flat layers of molybdenum metal atoms sandwiched above and belo

New York University physicists have applied a ground-breaking nanotechnology method to create three-dimensional quasicrystals, highly ordered structures that, unlike conventional crystals, never repeat themselves.
Metallic quasicrystals created from exotic alloys have shown promise for storing hydrogen more efficiently than crystalline hosts. Their non-repeating structure has the potential to dramatically strengthen industrial and commercial products. The NYU quasicrystals, by