This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.

By using DNA molecules as scaffolds, scientists have created superconducting nanodevices that demonstrate a new type of quantum interference and could be used to measure magnetic fields and map regions of superconductivity.
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have fabricated and studied nanostructures consisting of pairs of suspended superconducting wires as tiny as 3 to 4 molecular diameters (typically 5 to 15 nanometers) in width. The team consisted of p

University of California scientists working at Los Alamos National Laboratory have developed a novel method for controlling and measuring electron spins in semiconductor crystals of GaAs (gallium arsenide). The work suggests an alternative–and perhaps even superior–method of spin manipulation for future generations of “semiconductor spintronic” devices.
In research published in today’s issue of the scientific journal Physical Review Letters, Scott Crooker and Darryl Smith

The re-entry module of the Foton-M2 spacecraft, which has been in low-Earth orbit for the last 16 days made a successful landing today in an uninhabited area 140 km south-east of the town of Kostanay in Kazakhstan, close to the Russian border at 09:37 Central European Time, 13:37 local time.
The unmanned Foton-M spacecraft, which was launched on 31 May from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, carried a European payload of 385 kg covering 39 experiments in fluid physics, biolo
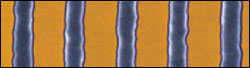
Straight edges, good. Wavy edges, bad. This simple description holds true whether you are painting the living room or manufacturing nanoscale circuit features.
In a technical paper* published in June, researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and SEMATECH describe an improved method for determining nanoscale “linewidth roughness,” an important quality control factor in semiconductor fabrication. Their research shows that current industry measurement

Measurements of the intensity of light at different wavelengths can be made more accurately now, thanks to a new, simple method for correcting common instrument errors. The new method, developed by researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), will benefit fields such as color measurement, lighting development, remote sensing, biotechnology and astronomy.
The NIST method improves the measurement accuracy of spectrometers, devices that measure optical

The second 20-metre antenna boom of the MARSIS instrument on board Mars Express was successfully – and smoothly – deployed, confirmed today by the ground team at ESA’s European Space Operations Centre.
The command to deploy the second MARSIS boom was given to the spacecraft at 13:30 CEST on 14 June 2005. Shortly before the deployment started, Mars Express was set into a slow rotation to last 30 minutes during and after the boom extension. This rotation allowed all the boom’s hing