This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.

In the current issue of Science magazine (Vol. 306, Dec. 3, 2004), scientists from the Max-Born-Institute for Nonlinear Optics and Short Pulse Spectroscopy (MBI) in Berlin, Germany, report the direct observation of atomic motions in a semiconductor nanostructure. They use a novel, laser-driven source for ultrashort x-ray pulses to take a movie of atomic motions in a semiconductor nanostructure. “We can observe changes on ultrashort timescales with our femtosecond x-ray diffraction setup”, says
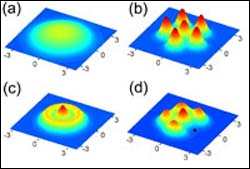
Researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology have unveiled a fundamental change in the properties of matter. The theoretical finding, that bosons placed in two-dimensional harmonic traps will crystallize when the strength of their repulsive interactions is increased, appears in the December 3 issue of the journal Physical Review Letters (volume 93, article 230405, 2004).
One of two categories of elementary particles, bosons typically form cloudy aggregates called Bose-E

Cutting edge research at the University of Ulster into how to make complex computers and communications systems manage themselves could power the next generation of US space probes, it was revealed today.
Roy Sterritt, from the University’s Computer Science Research Institute, was today addressing NASA scientists in Washington about his research.
Mr Sterritt said that current computing networks are now so complex and difficult to manage that by 2010, 220 million people

Close encounter may explain some objects beyond Neptune
Computer simulations show a close encounter with a passing star about 4 billion years ago may have given our solar system its abrupt edge and put small, alien worlds into distant orbits around our sun.
The study, which used a supercomputer at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif., was published in the Dec. 2 issue of the journal Nature by physicist Ben Bromley of the University of Utah and astron

A practical method for automatically correcting data-handling errors in quantum computers has been developed and demonstrated by physicists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
Described in the Dec. 2, 2004, issue of the journal Nature, the NIST work is the first demonstration of all the steps of error correction for quantum computers, a futuristic, potentially very powerful form of computing that uses the quantum properties of atoms or other particles as

Very Large Telescope Takes Snapshots of Two Grand-Design Spiral Galaxies Images of beautiful galaxies, and in particular of spiral brethren of our own Milky Way, leaves no-one unmoved. It is difficult indeed to resist the charm of these impressive grand structures. Astronomers at Paranal Observatory used the versatile VIMOS instrument on the Very Large Telescope to photograph two magnificent examples of such “island universes”, both of which are seen in a southern constellation wit