This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.

A NASA Chandra X-ray Observatory image has revealed a complex of several intergalactic hot gas clouds in the process of merging. The superb Chandra spatial resolution made it possible to distinguish individual galaxies from the massive clouds of hot gas. One of the clouds, which envelopes hundreds of galaxies, has an extraordinarily low concentration of iron atoms, indicating that it is in the very early stages of cluster evolution.
“We may be seeing hot intergalactic gas in a

Network could operate 100 times faster
Canadian researchers have shown that nanotechnology can be used to pave the way to a supercharged Internet based entirely on light. The discovery could lead to a network 100 times faster than today’s.
In a study published today in Nano Letters, Professor Ted Sargent and colleagues advance the use of one laser beam to direct another with unprecedented control, a featured needed inside future fibre-optic networks. “This finding showc
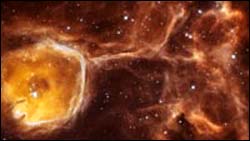
Real geodes are handball-sized, hollow rocks that start out as bubbles in volcanic or sedimentary rock. Only when these inconspicuous round rocks are split in half by a geologist, do we get a chance to appreciate the inside of the rock cavity that is lined with crystals. In the case of Hubble’s 35 light-year diameter ’celestial geode’ the transparency of its bubble-like cavity of interstellar gas and dust reveals the treasures of its interior.
The object, called N44
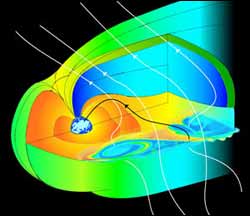
A bevy of satellites buzzing around in the Earth’s magnetosphere has found at least part of the answer to a long-standing puzzle about the source of the charged particles that feed the aurora.
The charged particles come from explosions on the sun and smash into the Earth’s magnetic field, which repels the bulk of them. But many slip through, often via a physical process called magnetic reconnection, where the magnetic field traveling with the particles breaks and reconnect

A new method for looking at the composition of comets using ground-based telescopes has been developed by chemists at UC Davis. Remnants from the formation of our solar system, the makeup of comets gives clues about how the Earth and other planets formed.
William Jackson, professor and chair of chemistry at UC Davis; researchers Alexandra Scodinu and Dadong Xu; and Anita Cochran of the University of Texas at Austin have developed methods to use visible and ultraviolet spectroscopy

ESA’s Mars Express has relayed pictures from one of NASA’s Mars rovers for the first time, as part of a set of interplanetary networking demonstrations. The demonstrations pave the way for future Mars missions to draw on joint interplanetary networking capabilities. ESA and NASA planned these demonstrations as part of continuing efforts to cooperate in space exploration.
On 4 August at 14:24 CEST, as Mars Express flew over one of NASA’s Mars exploration rovers, Opportunity, i