This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.

After a quiet, six-and-a-half-year, 2.2-billion-mile journey to Saturn aboard NASA’s Cassini spacecraft, the University of Chicago’s dust detector will soon begin its attempt to help unravel the mystery of the planet’s legendary rings one tiny particle at a time.
Cassini will become the first spacecraft ever to enter Saturn’s orbit at precisely 9:30 p.m. CDT June 30. NASA launched Cassini in October 1997. The University’s instrument, called the High Rate Detector, has quietly recorded spora
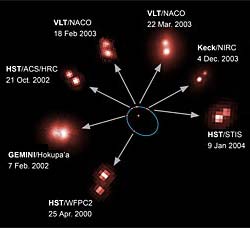
An international team of astronomers using the world’s biggest telescopes have directly measured the mass of an ultra-cool brown dwarf star and its companion dwarf star for the first time. Barely the size of the planet Jupiter, the dwarf star weighs in at just 8.5 percent of the mass of our Sun. This is the first ever mass measurement of a dwarf star belonging to a new stellar class of very low mass ultra-cool dwarf stars. The observation is a major step towards our understanding of the types of

Hottest body outside the sun
The hottest spot in the solar system is neither Mercury, Venus, nor St. Louis in the summer. Io, one of the four satellites that the Italian astronomer Galileo discovered orbiting Jupiter almost 400 years ago, takes that prize. The Voyager spacecraft discovered volcanic activity on Io over 20 years ago and subsequent observations show that Io is the most volcanically active body in the solar system. The Galileo spacecraft, named in honor of the astronomer

This amazing high-resolution image of Phoebe’s pitted surface was taken very near the closest approach by the NASA/ESA/ASI Cassini-Huygens spacecraft.
It shows a crater with a diameter of 13 kilometres and a debris-covered floor. Part of another crater of similar size is visible at left, as is part of a larger crater at the top and many scattered smaller craters.
The radial streaks in the crater are due to downslope movements of loose fragments from impact ejecta (material thrown

Images collected during the Cassini-Huygens close fly-by of Saturn’s moon Phoebe give strong evidence that the tiny moon may be rich of ice and covered by a thin layer of darker material.
Its surface is heavily battered, with large and small craters. It might be an ancient remnant of the formation of the Solar System.
On Friday 11 June, at 21:56 CET, the Cassini-Huygens spacecraft flew by Saturn’s outermost moon Phoebe, coming within approximately 2070 kilometres of the satell

An international team of astronomers, led by Hervé Bouy from the Max Planck Institute, Garching, Germany and the Observatoire de Grenoble, France, have for the first time measured the mass of an ultra-cool brown dwarf star. The team performed the measurements using four of the most powerful telescopes available. This is the first-ever mass measurement of an L-type star belonging to the new stellar class of very low-mass stars, discovered a few years ago. With a mass of 6.6% of the solar mass, this ce