This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
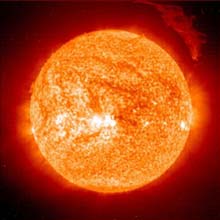
On Friday, 12 March 2004, the Sun ejected a spectacular ’eruptive prominence’ into the heliosphere. SOHO, the ESA/NASA solar watchdog observatory, faithfully recorded the event.
This ’eruptive prominence’ is a mass of relatively cool plasma, or ionised gas. We say ’relatively’ cool, because the plasma observed by the Extreme-ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (EIT) on board SOHO was only about 80 000 degrees Celsius, compared to the plasma at one or two milli

Talk about precision. New measurements of key wavelengths of ultraviolet light — down to a few millionths of a nanometer — are among the most precise ever reported and are improving calibrations of microlithography tools used in making integrated circuits such as those in computer chips.
The dimensions involved are 10,000 times smaller than hydrogen atoms, the smallest of all atoms.
To make the measurements, physicists at the National Institute of Standards and Technolo
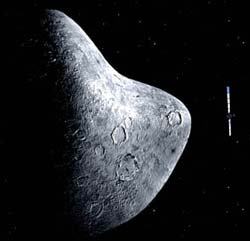
ESA PR 15-2004. Today the Rosetta Science Working Team has made the final selection of the asteroids that Rosetta will observe at close quarters during its journey to Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko. Steins and Lutetia lie in the asteroid belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
Rosetta’s scientific goals always included the possibility of studying one or more asteroids from close range. However, only after Rosetta’s launch and its insertion into interplanetary orbit could the

Astronomers today unveiled the deepest portrait of the visible Universe ever achieved by humankind. Called the Hubble Ultra Deep Field (HUDF), the million-second-long exposure reveals the first galaxies to emerge from the so-called ’dark ages’, the time shortly after the ’Big Bang’ when the first stars reheated the cold, dark Universe. The new image should offer unprecedented insights into what types of objects reheated the Universe long ago.
This historic new view is actually made up by t
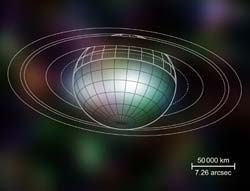
The Chandra X-ray Observatory is a space observatory dedicated to X-ray astronomy. Launched on July 23rd, 1999, this X-ray telescope is particularly dedicated to the observation of high-energy sources in the universe. It has also been used to study the following solar system objects: the Moon, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and even the Comet C/1999 S4 LINEAR.
Using Chandra, J.-U. Ness and his colleagues detected an unambiguous X-ray emission from the planet Saturn for the first time. A few years a

Ann Nguyen chose a risky project for her graduate studies at Washington University in St. Louis. A university team had already sifted through 100,000 grains from a meteorite to look for a particular type of stardust — without success.
In 2000, Nguyen decided to try again. About 59,000 grains later, her gutsy decision paid off. In the March 5 issue of Science, Nguyen and her advisor, Ernst K. Zinner, Ph.D., research professor of physics and of earth and planetary sciences, both in Arts & Sc