This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.

When Earth’s sun expands into a red giant star in roughly five billion years, long after Earth has become uninhabitable, the hydrogen core will be burned out and the bloated outer shell will be cool and murky.
But according to new research by the University of Colorado at Boulder, such red giants still retain surface magnetic storms and coronas — the very hot and patchy outer atmosphere of the sun and sun-like stars — at temperatures of millions of degrees Fahrenheit that often signal

One and a half billion years ago the small, inconspicuous galaxy Messier 82 (M82) almost smashed into its large, massive neighbour galaxy Messier 81 (M81), causing a frenzy of star formation.
New research by astronomers from the Universities of Cambridge and Utrecht, Netherlands, has now discovered an elusive phenomenon in this violent “starburst” area. About 100 star clusters have been discovered that are believed to be the ancestors of the so-called “globular clusters” thought to be the ol

ESA’s Rosetta will be the first mission to orbit and land on a comet, one of the icy bodies that travel throughout the Solar System and develop a characteristic tail when they approach the Sun. Rosetta is scheduled to be launched on-board an Ariane-5 rocket in January 2003 from Kourou, French Guiana. A decision on the launch date will be taken by Tuesday 14 January (see Arianespace press release N° 03/02 of 7 January 2003 or at http:www.arianespace.com).
The mission’s target is Comet Wi

A vast, but previously unknown structure has been discovered around our own Milky Way galaxy by an international team of astronomers. The announcement is being made at the American Astronomical Society’s meeting in Seattle, Washington, on behalf of Drs Annette Ferguson, Rodrigo Ibata, Mike Irwin, Geraint Lewis and Nial Tanvir. Their observations suggest that there is a giant ring of several hundred million stars surrounding the main disk of the Milky Way. Despite its size, the ring has not been

This Chandra X-ray Observatory image of the supermassive black hole at the Milky Way’s center, a.k.a. Sagittarius A* or Sgr A*, was made from the longest X-ray exposure of that region to date. In addition to Sgr A* more than two thousand other X-ray sources were detected in the region, making this one of the richest fields ever observed.
During the two-week observation period, Sgr A* flared up in X-ray intensity half a dozen or more times. The cause of these outbursts is not understood
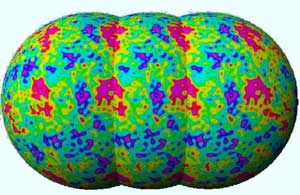
Cosmologists hope to “hear the shape of space”, namely its topology, by analyzing in detail the temperature fluctuations in the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB). An international team of cosmologists, including researchers from l’Observatoire de Paris, has recently developped a model for the vibrations of the universe. For the first time [1], they have simulated high resolution CMB maps containing the signatures of a wide class of topologies, for comparison with the forthcoming MAP satell