This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
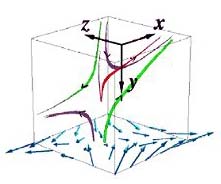
In work that promises new insights into the cosmos and fusion-energy production alike, physicists have reported they have made the first three-dimensional laboratory measurements of magnetic reconnection, the main process by which magnetic fields release energy in the universe.
Magnetic reconnection is the phenomenon in which magnetic energy in a plasma is rapidly converted to heat and jets of energetic particles. This process is thought to heat the solar corona, the outer atmosphere of the

Working toward the vision of generating clean energy from nuclear fusion, researchers have successfully imploded fuel capsules by bombarding them with intense x-rays. The results show that the process generates significant fusion and that the implosion method looks capable of generating large-scale energy production.
The process works by bombarding two millimeter (about 1/16th inch) fuel capsules with intense x-rays from Sandia National Laboratories Z-pinch machine. The x-rays, impacting fro

Duke University researchers have created an ultracold gas that has the startling property of bursting outward in a preferred direction when released. According to the researchers, studying the properties of the “lopsided” gas will yield fundamental insights into how matter holds itself together at the subatomic level.
Also, the research team leader said their data suggests the possibility that the gas is exhibiting a never-before-seen kind of superfluidity – a property in which matter at ex

A fraction of a second after the Big Bang, all the primordial soup of matter in the Universe was `broken` into its most fundamental constituents. It was thought to have disappeared forever. However scientists strongly suspect that the exotic soup of dissolved matter can still be found in today`s Universe, in the core of certain very dense objects called neutron stars.
With ESA`s space telescope XMM-Newton, they are now closer to testing this idea. For the first time, XMM-Newton has been able
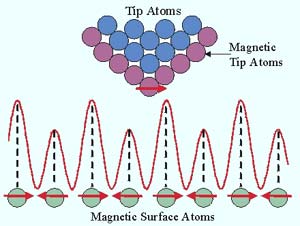
Scientists and engineers build the transistors that run televisions, radios and similar electronic devices based on the moving electric charges of electrons. But the electron also has another key property: a magnetic “spin” that scientists believe could be exploited to develop faster, smaller and more efficient devices.
The first step is to determine the magnetic properties of materials that could be used to create futuristic nanoscale devices, a task that has escaped scientists until now.

Researchers from the University of Michigan and RIKEN, a research institute in Japan, say the biological motors that nature uses for intracellular transport and other biological functions inspired them to create a whole new class of micro-devices for controlling magnetic flux quanta in superconductors that could lead to the development of a new generation of medical diagnostic tools.
As integrated circuits become smaller and smaller, it becomes increasingly difficult to create the many “gu