Photoinduced large polaron transport and dynamics
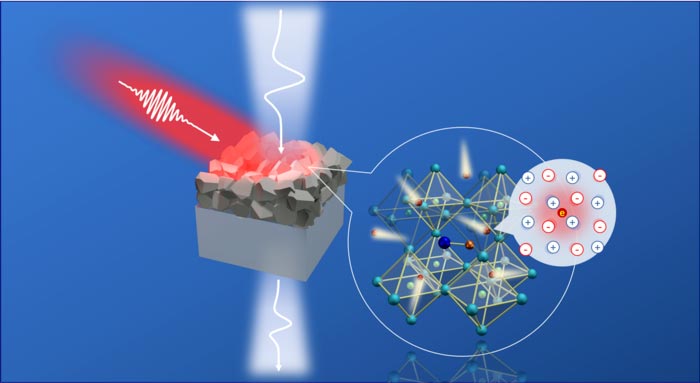
The photoexcited charge carrier is “dressed” by the local lattice distortion, which is revealed by ultrafast conductivity measurements using terahertz transient.
Credit by Zuanming Jin, Yan Peng, Yuqing Fang, Zhijiang Ye, Zhiyuan Fan, Zhilin Liu, Xichang Bao, Heng Gao, Wei Ren, Jing Wu, Guohong Ma, Qianli Chen, Chao Zhang, Alexey V. Balakin, Alexander P. Shkurinov, Yiming Zhu, Songlin Zhuang
… in organic-inorganic hybrid lead halide perovskite with terahertz probes.
Organic-inorganic hybrid metal halide perovskites (MHPs) have attracted tremendous attention for optoelectronic applications. For example, cost-effective solar cells, solid-state lighting, memristors, and ultrafast spin switches in spintronics have recently been designed using MHPs. Despite the promise of the material, many questions remain regarding the nature and mobility of charge carriers in MHPs, which require further understanding.
Researchers from the University of shanghai for science and technology, in collaboration with Qingdao institute of bioenergy and bioprocess technology, Shanghai University, Shanghai institute of technical physics, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, and Lomonosov Moscow State University, now report photoinduced large polaron transport and dynamics in organic-inorganic hybrid lead halide perovskite with terahertz probes.
The researchers experimentally identify the photocarriers-optical phonon coupling in CH3NH3PbI3 (MAPbI3) polycrystalline grains, by using optical-pump and terahertz-electromagnetic probe spectroscopy. The photoinduced charge carrier, together with the surrounding lattice distortion over several lattice constants, forms a quasi-particle – a polaron. Using the Drude-Smith-Lorentz model along with the Frӧhlich-type electron-phonon coupling, the researchers determine the effective mass and scattering parameters of photogenerated polaronic carriers. According to the polaron mass enhancement, the polycrystalline nature of the material, and the presence of defects, the large polaron mobility is calculated on the order of ~80 cm2V−1s−1.
Furthermore, the researchers reveal that the formation of large polarons in MAPbI3 protects the charge carriers from scattering with polycrystalline grain boundaries or defects and explains the long lifetime of photoconductivity. The findings provide insights into the polaronic nature of charge carriers in MAPbI3 materials, which is relevant for both fundamental researches and device applications. The results are published in the journal Light: Science & Applications.
Journal: Light Science & Applications
DOI: 10.1038/s41377-022-00872-y
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…


