Physicists generate new nanoscale spin waves
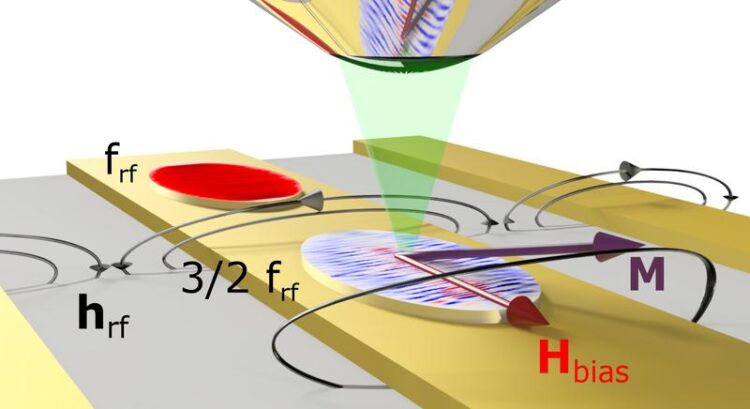
Illustration of the experiment
Credit: Dreyer et al, Nature Communications (CC-BY-SA 4.0)
Strong alternating magnetic fields can be used to generate a new type of spin wave that was previously just theoretically predicted. This was achieved for the first time by a team of physicists from Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU). They report on their work in the scientific journal “Nature Communications” and provide the first microscopic images of these spin waves.
The basic idea of spintronics is to use a special property of electrons – spin – for various electronic applications such as data and information technology. The Spin is the intrinsic angular momentum of electrons that produces a magnetic moment. Coupling these magnetic moments creates the magnetism that could ultimately be used in information processing. When these coupled magnetic moments are locally excited by a magnetic field pulse, this dynamic can spread like waves throughout the material. These are referred to as spin waves or magnons.
A special type of those waves is at the heart of the work of the physicists from Halle. Normally, the non-linear excitation of magnons produces integers of the output frequency – 1,000 megahertz becomes 2,000 or 3,000, for example. “So far, it was only theoretically predicted that non-linear processes can generate spin waves at higher half-integer multiples of the excitation frequency ,” explains Professor Georg Woltersdorf from the Institute of Physics at MLU. The team has now been able to show experimentally which conditions are needed in order to generate these waves and to control their phase. Phase is the state of the oscillation of a wave at a certain point and time. “We are the first to to confirm these excitations in experiments and have even been able to map them,” says Woltersdorf.
According to the physicist, the waves can be generated in two stable phase states which means this discovery could potentially be used in data processing applications, since computers, for example, also use a binary system.
The study was funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation, DFG).
Originalpublikation:
Study: Dreyer R. et al. Imaging and phase-locking of non-linear spin waves. Nature Communications (2022). doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32224-0
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-32224-0
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…


