Quantum Sensors Decipher Magnetic Ordering in a New Semiconducting Material
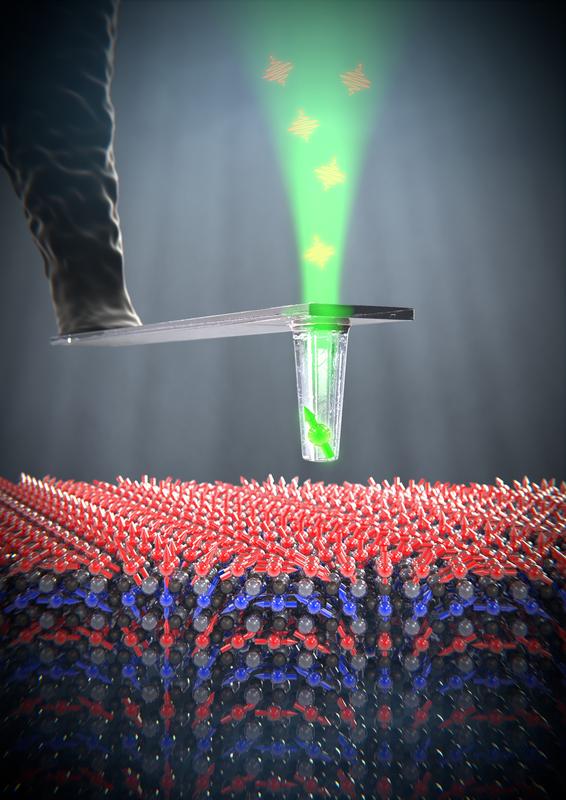
An individual electron spin in a quantum sensor reacts to the magnetic field of a thin film of bismuth ferrite. Bild: Universität Basel, Departement Physik
Multiferroics are materials that simultaneously react to electric and magnetic fields. These two properties are rarely found together, and their combined effect makes it possible to change the magnetic ordering of materials using electric fields.
This offers particular potential for novel data storage devices: multiferroic materials can be used to create nanoscale magnetic storage media that can be deciphered and modified using electric fields.
Magnetic media of this kind would consume very little power and operate at very high speeds. They could also be used in spintronics – a new form of electronics that uses electrons’ spin as well as electrical charge.
Spiral magnetic ordering
Bismuth ferrite is a multiferroic material that exhibits electric and magnetic properties even at room temperature. While its electrical properties have been studied in depth, there was no suitable method for representing magnetic ordering on the nanometer scale until now.
The group led by Georg-H.-Endress Professor Patrick Maletinsky, from the Swiss Nanoscience Institute and the University of Basel’s Department of Physics, has developed quantum sensors based on diamonds with nitrogen vacancy centers. This allowed them, in collaboration with colleagues at the University of Montpellier and the University Paris-Saclay in France, to depict and study the magnetic ordering of a thin bismuth ferrite film for the first time, as they report in Nature.
Knowing how the electron spins behave and how the magnetic field is ordered is of crucial importance for the future application of multiferroic materials as data storage.
The scientists were able to show that bismuth ferrite exhibits spiral magnetic ordering, with two superimposed electron spins (shown in red and blue in the image) adopting opposing orientations and rotating in space, whereas it was previously assumed that this rotation took place within a plane. According to the researchers, the quantum sensors now show that a slight tilt in these opposing spins leads to spatial rotation with a slight twist.
“Our diamond quantum sensors allow not only qualitative but also quantitative analysis. This meant we were able to obtain a detailed picture of the spin configuration in multiferroics for the first time,” explains Patrick Maletinsky. “We are confident that this will pave the way for advances in research into these promising materials.”
Vacancies with special properties
The quantum sensors they used consist of two tiny monocrystalline diamonds, whose crystal lattices have a vacancy and a nitrogen atom in two neighboring positions. These nitrogen vacancy centers contain orbiting electrons whose spins respond very sensitively to external electric and magnetic fields, allowing the fields to be imaged at a resolution of just a few nanometers.
Scientists at the University of Montpellier took the magnetic measurements using the quantum sensors produced in Basel. The samples were supplied by experts from the CNRS/Thales laboratory at University Paris-Saclay, who are leading lights in the field of bismuth ferrite research.
Quantum sensors for the market
The quantum sensors used in the research are suitable for studying a wide range of materials, as they provide precisely detailed qualitative and quantitative data both at room temperature and at temperatures close to absolute zero.
In order to make them available to other research groups, Patrick Maletinsky founded the start-up Qnami in 2016 in collaboration with Dr. Mathieu Munsch. Qnami produces the diamond sensors and provides application advice to its customers from research and industry.
Original article
I. Gross, W. Akhtar, V. Garcia, L. J. Martínez, S. Chouaieb, K. Garcia, C. Carrétéro, A. Barthélémy, P. Appel, P. Maletinsky, J.-V. Kim, J. Y. Chauleau, N. Jaouen, M. Viret, M. Bibes, S. Fusil and V. Jacques
Real-space imaging of non-collinear antiferromagnetic order with a single spin magnetometer
Nature (2017), doi: 10.1038/nature23656
Further information
Prof. Patrick Maletinsky, University of Basel, Department of Physics, tel. +41 61 207 37 63, email: patrick.maletinsky@unibas.ch
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.unibas.chAll latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Redefining Cancer Science: Rodents, Humans, and the PD-1 Puzzle
Results of a comprehensive analysis refute assumptions that a key immune checkpoint receptor functions the same in rodents and humans The Discovery of PD-1: A Milestone in Cancer Treatment Since…

Heart Surgery Risks: Low BP Linked to Postoperative Kidney Injury
First large cohort study at the Heart and Diabetes Center NRW awarded – Hilke Jung presents research project at the FoRUM conference of the Ruhr University Bochum A working group…

Microbial Secrets: Boost Plant Growth with the Power of Soil Bacteria
To stay healthy, plants balance the energy they put into growing with the amount they use to defend against harmful bacteria. The mechanisms behind this equilibrium have largely remained mysterious….



