Radon inferior to radium for electric dipole moments (EDM) searches
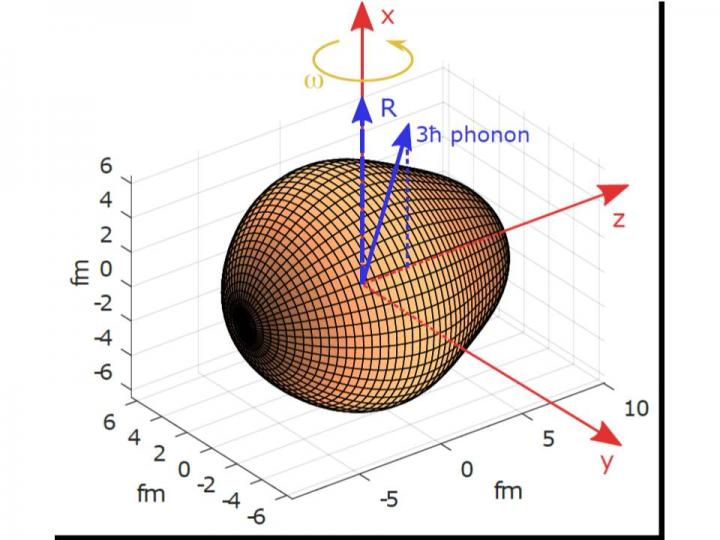
Cartoon illustrating how the octupole phonon vector aligns with the rotation (R) vector (which is orthogonal to the rotating body’s symmetry axis) so that I = R + 3ℏ and Δix=3ℏ Credit: University of Liverpool
Short lived isotopes of both radon and radium have both been identified as potential candidates for measuring EDM in atoms.
However, in a paper published in Nature Communications researchers conclude, for the first time, that radon atoms provide less favourable conditions for the enhancement of a measurable atomic EDM than radium.
The researchers exploited the ISOLDE facility at CERN to accelerate beams of radioactive radon ions and were able to measure the properties of rotating radon nuclei.
The experiments showed that the radon isotopes 224Rn and 226Rn vibrate between a pear shape and its mirror image but do not possess static pear-shapes in their ground states. This behaviour is quite different to their neighbouring radium isotopes that are permanently deformed into the shape of a pear.
Liverpool Professor of Physics, Peter Butler, who is the lead author of the paper and spokesperson of the collaboration that carried out the research, said: “This research builds on our experimental observation of nuclear pear shapes in 2013.
“We find that certain radon isotopes vibrate between a pear shape and its mirror image. This is in contrast to radium, where we have previously shown that some radium isotopes are permanently deformed into the shape of a pear.
“This finding is important for searches for EDMs in atoms which, if measurable, would require revisions of the Standard Model that could explain the matter-antimatter asymmetry in the universe.”
The paper `The observation of vibrating pear-shapes in radon nuclei' (doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10494-5) is published today in Nature Communications.
The experiments were conducted at HIE-ISOLDE at CERN, Switzerland in collaboration with University of the West of Scotland, UK; University of the Western Cape, South Africa; TRIUMF, Canada; Lund University, Sweden; University of Michigan, USA; INFN Legnaro, Italy; KU Leuven, Belgium; University of Guelph, Canada; University of Cologne, Germany; TU Darmstadt, Germany; University of Warsaw, Poland; University of Jyvaskyla, Finland; University of Oslo, Norway; University of York, UK; JINR Dubna, Russia; CSIC Madrid, Spain; CEA Saclay, France.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10494-5All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Bad bacteria can trigger painful gut contractions
UO researchers unravel the mechanism behind an unpleasant symptom of digestive problems. After a meal of questionable seafood or a few sips of contaminated water, bad bacteria can send your…

No cavity, no party: Free-space atoms give superradiant transition a pass
Isolated atoms in free space radiate energy at their own individual pace. However, atoms in an optical cavity interact with the photons bouncing back and forth from the cavity mirrors,…

How SMEs are Successfully Using Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has established a strong presence across industries, large and small. The “VoBaKI” research project has empowered small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with an innovative tool to independently…



