Watching the birth and death of exotic molecules
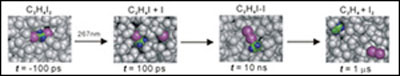
These four pictures show how the C2 H4 I2 molecule changes shape and composition in a very short period of time.
Researchers from Korea, Italy, France and the ESRF have just observed how a molecule changes structure after being hit with a short flash of laser light. Thanks to very intense pulses of X-rays from the synchrotron and novel data analysis, they were able to confirm a long standing hypothesis regarding the evolution of this molecule. The results are published in the 14 July Science Express, the online counterpart of the journal Science.
The experiment was started by dissolving the molecule C2H4I2 in liquid methanol and then hitting it with a short laser pulse. This excited the molecule, which then cooled down while releasing heat into the surrounding liquid. As a consequence, the temperature rose and the liquid started to expand in response to the increase in temperature. The absorption of light triggered a chemical reaction, which the researchers studied with picosecond time resolution. They measured the change in shape and composition as early as 100 picoseconds after the initial explosion, then at 10 nanoseconds after, then 1 microsecond and so on. All these dancing atoms were confined to a tiny “dance floor” with a radius of about 6 Ångstroms (0.6 nanometres).
Once excited, one of the bonds in the molecule was elongated. The excited molecule then had two fates. One of them was to bounce back to the hot ground-state C2H4I2, which is surrounded by solvent molecules. In the second case, the excited molecule C2H4I2 dissociates and forms C2H4I and I. There are two hypotheses on the structure of the C2H4I radical. The first possibility is that the radical retains a classical structure very similar to the initial structure of C2H4I2-(the anti structure). The second possibility is that the iodine combines with the two carbon molecules in a triangular geometry (bridge structure). This bridged conformation is the structure that prevails, according to the new measurements at the ESRF. The bridged structure has long been hypothesised to explain stereochemical control, but has never been observed directly until now. This research is the outcome of two-years of work involving a Korean research group from KAIST lead by Hyotcherl Ihee and the ID09B team lead by Michael Wulff.
Researchers at the ESRF had already studied the dissociation of molecular iodine some months ago and defined, theoretically and experimentally, the principal reaction channels in photo reactions in liquids. This new work is an important step forward since C2H4I2 is a bigger and more complex molecule and, more importantly, its photoreaction proceeds though novel molecular structures that have never been seen before. This research opens a new door to the study of chemical reactions in liquids. Hyotcherl Ihee, first author of the paper, believes that this technique will be used increasingly in the future: “We envisage to expand it to study other samples, such as nanomaterials and proteins”.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.esrf.fr/NewsAndEvents/PressReleases/PRESSRELEASEID09/All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

How marine worms regenerate lost body parts
The return of cells to a stem cell-like state as the key to regeneration. Many living organisms are able to regenerate damaged or lost tissue, but why some are particularly…

Nano-scale molecular detective
New on-chip device uses exotic light rays in 2D material to detect molecules. Researchers have developed a highly sensitive detector for identifying molecules via their infrared vibrational “fingerprint”. Published in Nature…

Novel CAR T-cell therapy
… demonstrates efficacy and safety in preclinical models of HER2-positive solid tumors. The p95HER2 protein is found expressed in one third of HER2+ tumors, which represent 4% of all tumors….



