Researchers measure the global magnetic field in solar corona for the first time
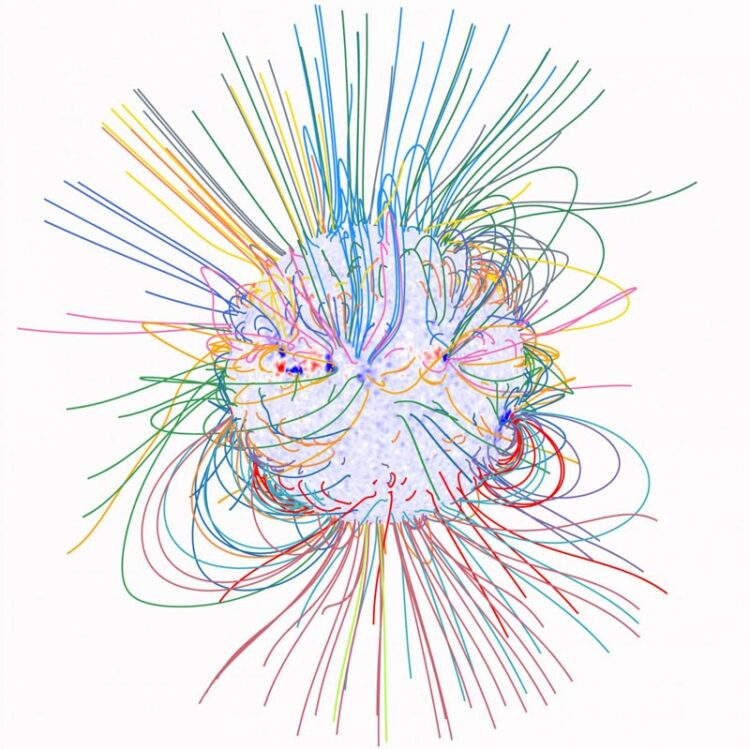
Magnetic field of the Sun calculated from a theoretical model
Credit: YANG Zihao and TIAN Hui
The Sun is a magnetized star. Its magnetic field is essentially three dimensional and it occupies all layers of the solar atmosphere. However, routine measurements of the solar magnetic field have only been achieved at the photospheric level, or the solar surface.
Lacking precise knowledge about the magnetic field in the outermost solar atmosphere, the corona, has impeded our understanding of the solar magnetism and many phenomena in the solar atmosphere.
An international team led by TIAN Hui, a professor from both Peking University and National Astronomical Observatories of Chinese Academy of Sciences (NAOC), has measured the global magnetic field of the solar corona for the first time. The study was published in Science on August 7.
The team used observations from the Coronal Multi-channel Polarimeter (CoMP), an instrument operated by the High Altitude Observatory, National Center for Atmospheric Research, USA.
More than 20 years ago, a technique called coronal seismology or magneto-seismology has been introduced for coronal magnetic field measurements. This method makes use of some types of oscillations or waves that are observed in coronal structures.
However, these oscillations/waves are just occasionally observed in small regions of the corona, and thus their potential for magnetic field measurements is limited.
CoMP is a coronagraph with a 20-cm aperture. It can observe the solar corona using the Fe XIII 1074.7 nm and 1079.8 nm infrared spectral lines. The Doppler image sequence obtained from CoMP observations often reveal the prevalence of propagating periodic disturbances, indicating the ubiquitous presence of transverse plasma waves in the corona.
The team applied the magneto-seismology method to these pervasive waves. They extended the previously developed wave-tracking technique to the whole field of view, and obtained the distribution of the wave propagation speed in the global corona.
They also obtained a global map of the coronal density from observations of the two Fe XIII lines. Combing the maps of wave propagation speed and density, they mapped the magnetic field in the global corona.
“By applying this technique to CoMP-like instruments in the future, global coronal magnetic field maps could be routinely obtained, filling in the missing part of the measurements of the Sun’s global magnetism,” said Prof. TIAN.
Such measurements could provide critical information to advance our understanding of the physical mechanisms responsible for solar eruptions and the 11-year sunspot cycle.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Pinpointing hydrogen isotopes in titanium hydride nanofilms
Although it is the smallest and lightest atom, hydrogen can have a big impact by infiltrating other materials and affecting their properties, such as superconductivity and metal-insulator-transitions. Now, researchers from…

A new way of entangling light and sound
For a wide variety of emerging quantum technologies, such as secure quantum communications and quantum computing, quantum entanglement is a prerequisite. Scientists at the Max-Planck-Institute for the Science of Light…

Telescope for NASA’s Roman Mission complete, delivered to Goddard
NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope is one giant step closer to unlocking the mysteries of the universe. The mission has now received its final major delivery: the Optical Telescope…



