Researchers synthesize atomically precise diamond-shaped nanoclusters of silver
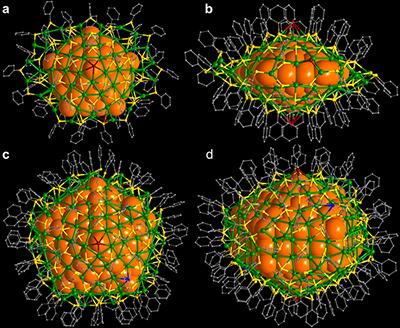
This figure shows: Upper row: (a) top and (b) side view of the 136-atom silver nanocluster. Lower row: (c) top and (d) side view of the 374-atom silver nanocluster. The metal cores of these clusters have a diameter of 2 and 3 nm, respectively. Silver atoms in the metal core are denoted by large orange sphere. The core is protected by a silver-thiol layer (green: silver; yellow: sulfur; carbon: gray). Courtesy of Nanfeng Zheng, Xiamen University. Credit: The University of Jyväskylä
These diamond-shaped nanoclusters (see Figure), consisting of a silver core of 2 to 3 nanometers and a protecting layer of silver atoms and organic thiol molecules, are the largest ones whose structure is now known to atomic precision. The research (1) was published in Nature Communications on 9 September 2016.
The nanoclusters where synthesized in Xiamen University in China and characterized by X-ray crystallography and electron microscopy in China, Australia and Germany. Their electronic structure and optical properties were studied computationally in the Nanoscience Center (NSC) of the University of Jyväskylä in Finland.
Gold nanoclusters that are stabilized by a thiol molecular layer have been known for decades, but only during the latest years silver clusters have attracted more interest in the research community. Silver is a desirable material for nanocluster synthesis since it is a cheaper metal than gold and its optical properties are better controllable for applications. However, synthesis recipes that would produce silver clusters that are stable for prolonged times are not so widely known as for gold.
“These largest atomically precise silver nanoclusters known thus far serve as excellent model systems to understand how silver nanoparticles grow,” says Professor Nanfeng Zheng whose research group prepared the clusters in Xiamen University in China. “The internal structure of the metal core is a combination of little crystallites of silver that are joined together to form a five-fold symmetric diamond-shape structure.”
“From a theoretical point of view these new clusters are very interesting,” says Academy Professor Hannu Häkkinen from the NSC in Jyväskylä. “These clusters are already big enough that they have properties similar to silver metal, such as strong absorption of light leading to collective oscillations of the electron cloud known as plasmons, yet small enough that we can study their electronic structure in detail. Much to our surprise, the calculations showed that electrons in the organic molecular layer take part actively in the collective oscillation of the silver electrons. It seems possible to then activate these clusters by light in order to do chemistry at the ligand surface.”
###
The other NSC researchers involved in the work were Xi Chen and Lauri Lehtovaara. The computational work was done at the CSC – the Finnish IT Centre for Science. The work at the University of Jyväskylä was supported by the Academy of Finland.
More information:
Academy Professor Hannu Häkkinen, University of Jyväskylä, Finland, hannu.j.hakkinen(at)jyu.fi tel:+358 400 247 973
Professor Nanfeng Zheng, Xiamen University, China, nfzheng(at)xmu.edu.cn
Academy of Finland Communications
Communications Specialist Leena Vähäkylä
tel. +358 295 335 139
firstname.lastname(at)aka.fi
References:
(1) H. Yang, Y. Wang, X. Chen, X. Zhao, L. Gu, H. Huang, J. Yan, C. Xu, G. Li, J. Wu, A.J. Edwards, B. Dittrich, Z. Tang, D. Wang, L. Lehtovaara, H. Häkkinen and N. Zheng, “Plasmonic twinned silver nanoparticles with molecular precision”, Nature Communications 7, 12809 (2016), published online 9 September 2016, doi: 10.1038/ncomms12809
Figure: Upper row: (a) top and (b) side view of the 136-atom silver nanocluster. Lower row: (c) top and (d) side view of the 374-atom silver nanocluster. The metal cores of these clusters have a diameter of 2 and 3 nm, respectively. Silver atoms in the metal core are denoted by large orange sphere. The core is protected by a silver-thiol layer (green: silver; yellow: sulfur; carbon: gray). Courtesy of Nanfeng Zheng, Xiamen University.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Hyperspectral imaging lidar system achieves remote plastic identification
New technology could remotely identify various types of plastics, offering a valuable tool for future monitoring and analysis of oceanic plastic pollution. Researchers have developed a new hyperspectral Raman imaging…

SwRI awarded $26 million to develop NOAA magnetometers
SW-MAG data will help NOAA predict, mitigate the effects of space weather. NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) recently awarded Southwest Research Institute a $26 million contract…

Protein that helps cancer cells dodge CAR T cell therapy
Discovery could lead to new treatments for blood cancer patients currently facing limited options. Scientists at City of Hope®, one of the largest and most advanced cancer research and treatment…



