Skyrmion Research: Braids of Nanovortices Discovered
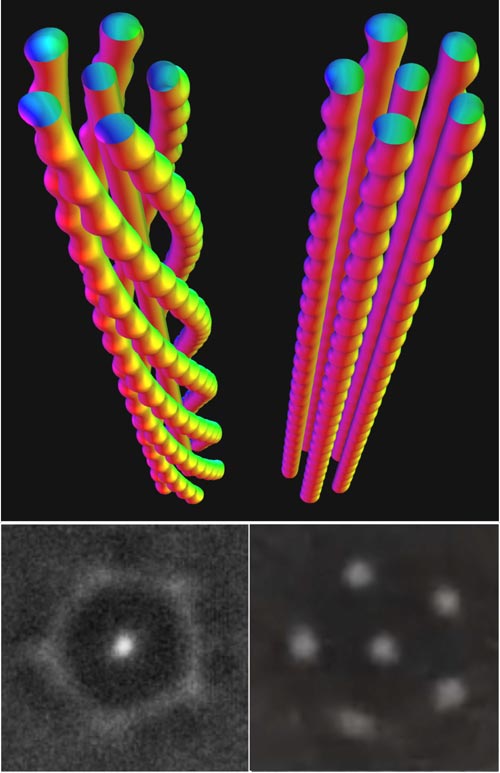
Researchers at Jülich have detected string-like structures made of skyrmions. Above, simulated models of six skyrmions at different magnetic field strengths; below, transmission electron microscope images of such structures observed in a thin film.
Copyright:
Forschungszentrum Jülich
A team of scientists from Germany, Sweden and China has discovered a new physical phenomenon: complex braided structures made of tiny magnetic vortices known as skyrmions. Skyrmions were first detected experimentally a little over a decade ago and have since been the subject of numerous studies, as well as providing a possible basis for innovative concepts in information processing that offer better performance and lower energy consumption. Furthermore, skyrmions influence the magnetoresistive and thermodynamic properties of a material. The discovery therefore has relevance for both applied and basic research.
Strings, threads and braided structures can be seen everywhere in daily life, from shoelaces, to woollen pullovers, from plaits in a child’s hair to the braided steel cables that are used to support countless bridges. These structures are also commonly seen in nature and can, for example, give plant fibres tensile or flexural strength. Physicists at Forschungszentrum Jülich, together with colleagues from Stockholm and Hefei, have discovered that such structures exist on the nanoscale in alloys of iron and the metalloid germanium.
These nanostrings are each made up of several skyrmions that are twisted together to a greater or lesser extent, rather like the strands of a rope. Each skyrmion itself consists of magnetic moments that point in different directions and together take the form of an elongated tiny vortex. An individual skyrmion strand has a diamater of less than one micrometre. The length of the magnetic structures is limited only by the thickness of the sample; they extend from one surface of the sample to the opposite surface.
Earlier studies by other scientists had shown that such filaments are largely linear and almost rod-shaped. However, ultra-high-resolution microscopy investigations undertaken at the Ernst Ruska-Centre in Jülich the theoretical studies at Jülich’s Peter Grünberg Institute have revealed a more varied picture: the threads can in fact twist together to varying degrees. According to the researchers, these complex shapes stabilise the magnetic structures, making them particularly interesting for use in a range of applications.
“Mathematics contains a great variety of these structures. Now we know that this theoretical knowledge can be translated into real physical phenomena,” Jülich physicist Dr. Nikolai Kiselev is pleased to report. “These types of structures inside magnetic solids suggest unique electrical and magnetic properties. However, further research is needed to verify this.”
To explain the discrepancy between these studies and previous ones, the researcher points out that analyses using an ultra-high-resolution electron microscope do not simply provide an image of the sample, as in the case of, for example, an optical microscope. This is because quantum mechanical phenomena come into play when the high energy electrons interact with those in the sample.
“It is quite feasible that other researchers have also seen these structures under the microscope, but have been unable to interpret them. This is because it is not possible to directly determine the distribution of magnetization directions in the sample from the data obtained. Instead, it is necessary to create a theoretical model of the sample and to generate a kind of electron microscope image from it,” explains Kiselev. “If the theoretical and experimental images match, one can conclude that the model is able to represent reality.” In ultra-high-resolution analyses of this kind, Forschungszentrum Jülich with its Ernst Ruska-Centre counts as one of the leading institutions worldwide.
Original publication:
Fengshan Zheng, Filipp N. Rybakov, Nikolai S. Kiselev, Dongsheng Song, András Kovács,
Haifeng Du, Stefan Blügel & Rafal E. Dunin-Borkowski;
Magnetic skyrmion braids;
Nature Communications (2021), DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-25389-7
Further Information:
Website Peter Grünberg Institute
Website Ernst Ruska-Centrum
Contakt:
Dr. Nikolai Kiselev
Peter Grünberg Institute/Institute for Advanced Simulations – Quantum Theory of Materials (PGI-1/IAS-1)
Tel. +49 2461 61-3328
E-Mail: n.kiselev@fz-juelich.de
Dr. Fengshan Zheng
Peter Grünberg Institute – Microstructure Research (PGI-5)/Ernst Ruska-Centre for Microscopy and Spectroscopy with Electrons – Physics of Nanoscale Systems (ER-C-1)
Tel. +49 2461 61-85232
E-Mail: f.zheng@fz-juelich.de
Press contact:
Angela Wenzik
Science Journalist
Forschungszentrum Jülich
Tel. +49 2461 61-6048
E-Mail: a.wenzik@fz-juelich.de
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…


