Smart bottle brushes
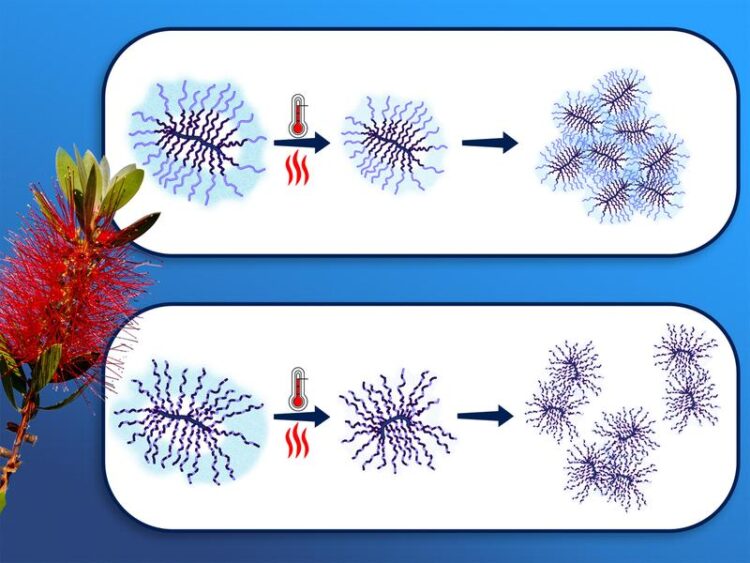
Thermoresponsive molecular brushes with propylene oxide/ethylene oxide copolymer side chains in aqueous solution.
Reiner Müller / TUM
Neutrons make structural changes in molecular brushes visible
They look like microscopic bottle brushes: Polymers with a backbone and tufts of side arms. This molecular design gives them unusual abilities: For example, they can bind active agents and release them again when the temperature changes. With the help of neutrons, a research team from the Technical University of Munich (TUM) has now succeeded to unveil the changes in the internal structure in course of the process.
“The structure of the bottle-brush polymers, which are only nanometers in size, cannot be investigated using classical optical methods: It can be seen that an aqueous solution containing these polymers becomes turbid at a certain temperature. But why this is the case, and how the backbone and the side arms stretch out into in the water or contract, has not yet been clarified,” reports Prof. Christine Papadakis.
There is a simple reason why scientists would like to know more about the inner life of bottle-brush polymers: The fluffy molecules, which consist of different polymer chains and abruptly change their solubility in water at a certain temperature, are promising candidates for a variety of applications.
For example, they could be used as catalysts to accelerate chemical reactions, as molecular switches to open or close tiny valves, or as transport media for medical drugs – the molecular brushes could thus bring pharmaceuticals to a center of inflammation and, because the temperature is elevated there, release them directly at the site of action.
However, the basic prerequisite for using the brush molecules is that their behavior can be programmed: Theoretically, chemists can use a combination of water-soluble and water-insoluble building blocks to determine precisely at what temperature the polymers clump together and the liquid in which they were just dissolved becomes cloudy. “In practice, however, you have to know exactly how and under what conditions the structure of the polymers changes if you want to design smart brush molecules,” explains Papadakis.
Neutrons reveal their molecular inner life
Together with her team in the Soft Matter Physics Group at the Technical University of Munich, she has now been able to visualize for the first time the changes that bottle-brush polymers with arms made of two different types of building blocks undergo when the temperature reaches the cloud point.
The scientists used neutron radiation from the Research Neutron Source Heinz Maier-Leibnitz (FRM II) on the campus Garching in a special instrument for small angle neutron scattering, which is operated by the Forschungszentrum Jülich
This method is particularly well suited for the investigation because neutrons are electrically neutral and therefore penetrate matter easily. There they are scattered by the atomic nuclei. The images of the brush molecules thus produced are more exact than x-rays and more detailed than images from scanning electron microscopy.
When brushes clump together
The thermoresponsive brush molecules studied by Papadakis’ team were synthesized by chemists from the National Hellenic Research Foundation in Greece and the Technische Universität Dresden, respectively.
In the first step, the samples were dissolved in water, then gradually heated up to the cloud point and irradiated with neutrons. A detector monitored the scattered radiation. From the scattering signal, the researchers were able to deduce the structural changes.
Depending on the structure of the polymers, water molecules split-off already before the cloud point was reached. At the cloud point itself, the molecular structure of the polymers collapsed. What remained were water-insoluble polymer coils, which formed loose or compact clusters depending on the residual water content.
“The results will help to develop bottle-brush polymers suitable for practical use,” the physicist is convinced. “If you know exactly how polymers change at the cloud point, you can optimize their chemical structure for different applications.”
The work was done in cooperation with the Faculty of Chemistry and Food Chemistry of the Technische Universität Dresden and the Theoretical and Physical Chemistry Institute of the National Hellenic Research Foundation, Greece. The project was funded by the German Research Foundation.
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Prof. Dr. Christine Papadakis
Professorship Soft Matter Physics
Technical University of Munich
James-Franck-Str. 1, 85748 Garching, Germany
Tel.: +49 89 289 12447 – E-mail: papadakis@tum.de
Originalpublikation:
Jia-Jhen Kang, Kaltrina Shehu, Clemens Sachse, Florian A. Jung, Chia-Hsin Ko, Lester C. Barnsley, Rainer Jordan, Christine M. Papadakis:
A molecular brush with thermoresponsive poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) side chains: a structural investigation
Colloid and Polymer Science, Aug. 5, 2020
Jia-Jhen Kang, Florian A. Jung, Chia-Hsin Ko, Kaltrina Shehu, Lester C. Barnsley, Fabian Kohler, Hendrik Dietz, Junpeng Zhao, Stergios Pispas, and Christine M. Papadakis:
Thermoresponsive Molecular Brushes with Propylene Oxide/ Ethylene Oxide Copolymer Side Chains in Aqueous Solution
Macromolecules 2020, 53, 4068−4081, Aug. 8, 2020
Weitere Informationen:
https://www.groups.ph.tum.de/en/softmatter/soft-matter-physics/ Homepage of the research group
https://www.tum.de/nc/en/about-tum/news/press-releases/details/36275/ Press release on the TUM website
https://www.frm2.tum.de/en/ Research Neutron Source Heinz Maier-Leibnitz
https://mlz-garching.de/englisch.html Heinz Maier-Leibnitz Zentrum
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04704-6 Original publication I.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.0c00263 Original publication II.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…


