The first observations of a space hurricane have been revealed in Earth’s upper atmosphere, confirming their existence and shedding new light on the relationship between planets and space.
Hurricanes in the Earth’s low atmosphere are known, but they had never before been detected in the upper atmosphere.
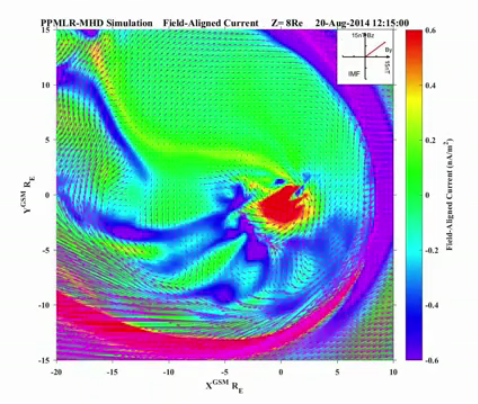
An international team of scientists led by Shandong University in China analysed observations made by satellites in 2014 to reveal a long-lasting hurricane, resembling those in the lower atmosphere, in the polar ionosphere and magnetosphere with surprisingly large energy and momentum deposition despite otherwise extremely quiet geomagnetic conditions.
The analysis allowed a 3D image to be created of the 1,000km-wide swirling mass of plasma several hundred kilometres above the North Pole, raining electrons instead of water.
Professor Qing-He Zhang, lead author of the research at Shandong University, said: “These features also indicate that the space hurricane leads to large and rapid deposition of energy and flux into the polar ionosphere during an otherwise extremely quiet geomagnetic condition, suggesting that current geomagnetic activity indicators do not properly represent the dramatic activity within space hurricanes, which are located further poleward than geomagnetic index observatories.”
Professor Mike Lockwood, space scientist at the University of Reading, said: “Until now, it was uncertain that space plasma hurricanes even existed, so to prove this with such a striking observation is incredible”.
“Tropical storms are associated with huge amounts of energy, and these space hurricanes must be created by unusually large and rapid transfer of solar wind energy and charged particles into the Earth’s upper atmosphere.
“Plasma and magnetic fields in the atmosphere of planets exist throughout the universe, so the findings suggest space hurricanes should be a widespread phenomena.”
Hurricanes often cause loss of life and property through high winds and flooding resulting from the coastal storm surge of the ocean and the torrential rains. They are characterised by a low-pressure centre (hurricane eye), strong winds and flow shears, and a spiral arrangement of towering clouds with heavy rains.
In space, astronomers have spotted hurricanes on Mars, and Saturn, and Jupiter, which are similar to terrestrial hurricanes in the low atmosphere. There are also solar gases swirling in monstrous formations deep within the sun’s atmosphere, called solar tornadoes. However, hurricanes had not been reported in the upper atmosphere of the planets in our heliosphere.
The space hurricane analysed by the team in Earth’s ionosphere was spinning in an anticlockwise direction, had multiple spiral arms, and lasted almost eight hours before gradually breaking down.
The team of scientists from China, the USA, Norway and the UK used observations made by four DMSP (Defense Meteorological Satellite Program) satellites and a 3D magnetosphere modelling to produce the image. Their findings were published in Nature Communications.
Professor Zhang added: “This study suggests that there are still existing local intense geomagnetic disturbance and energy depositions which is comparable to that during super storms. This will update our understanding of the solar wind-magnetosphere-ionosphere coupling process under extremely quiet geomagnetic conditions.
“In additional, the space hurricane will lead to important space weather effects like increased satellite drag, disturbances in High Frequency (HF) radio communications, and increased errors in over-the-horizon radar location, satellite navigation and communication systems.”
ADDITIONAL NOTES:
This cyclone-like auroral spot is also associated with 1) a spot-like strong upward FAC (with sometimes a FAC hole developed in the center), 2) zero horizontal flow near its center (the hurricane eye) as well as strong flow shears around the edges, 3) ion upflows, 4) enhanced electron temperature (about 1000 K enhancement), 5) a negative-to-positive bipolar magnetic structure (implying a circular magnetic field perturbation), 6) electron inverted-V acceleration to above 10 keV, and 7) large and rapid deposition of energy and flux into the polar ionosphere (much stronger precipitating electron energy flux than that during typical quiet and substorm conditions, and comparable to that during super storms). These features are very similar with the hurricane in low atmosphere, thus, the team analogically names it as “space hurricane”.
After detail analysing of the observation and simulation results, the team found that the magnetic reconnection will steadily occur at high latitude lobe region for an extended period of time during a several hour period of stable northward IMF and very low solar wind density and speed. After the lobe reconnection, the newly reconnected open field lines are draped by the solar wind to move dawnward and then tailward from the morning side to the afternoon side in the high-latitude lobe region and will gradually return to their previous positions and participate in a new cycle of magnetic reconnection. Their evolution will eventually form a cyclone-shaped funnel of FAC with multiple FAC arms and a clockwise circulation of the plasma flow, due to the pressure gradient and magnetic stresses on both sides of the funnel for completing the FACs and the flow shear and curvature of the circular flow. Inside the funnel, a corkscrew magnetic field forms with circular flow and upward FACs, which accelerate electrons that precipitate into the ionosphere and create the auroral spot with multiple arms. This means that the space hurricane opens a rapid energy transfer channel from space to the ionosphere and thermosphere.