Tailored probes for atomic force microscopes
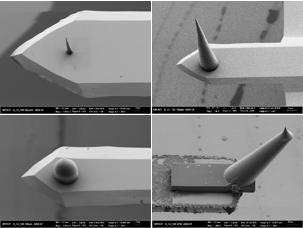
Optimally adapted probes for atomic force microscopes can now be produced by 3-D nanoprinting at KIT. Photos: KIT
Atomic force microscopes make the nanostructure of surfaces visible. Their probes scan the investigation material with finest measurement needles. KIT has now succeeded in adapting these needles to the application.
For any measurement task, e.g. for various biological samples, a suitable measurement needle can be produced. For production, 3D laser lithography, i.e. a 3D printer of structures in the nanometer size, is applied. This success has made it to the title page of the Applied Physics Letters journal. DOI: 10.1063/1.4960386
Atomic force microscopes are used to analyze surfaces down to the atomic level. The standard probes that have been applied for this purpose so far, however, are not suited for every use. Some examination objects require a special shape or a very long probe to scan deep depressions of the material. KIT researchers have now succeeded in producing probes that are optimally adapted to special requirements.
“Biological surfaces, such as the petals of tulips or roses, frequently have very deep structures with high hills,” says Hendrik Hölscher, Head of the Scanning Probe Technologies Group of KIT's Institute of Microstructure Technology. Commercially available probes typically are 15 micrometers, i.e. 15 thousandths of a millimeter, high, pyramid-shaped, and relatively wide, the physicist points out. Probes with other shapes are offered, but have to be produced manually, which makes them very expensive.
The KIT researchers have now succeeded in producing by means of 3D laser lithography tailored probes of any shape with a radius of 25 nanometers only, corresponding to 25 millionths of a millimeter. This process can be used to design and print in three dimensions any shape desired and has been known in the macroscopic area for some time already. On the nanoscale, this approach is highly complex. To obtain the three-dimensional structures desired, the researchers use the 3D lithography process developed by KIT and commercialized by Nanoscribe, a spinoff of KIT. This method is based on two-photon polymerization: Strongly focused laser pulses are applied to harden light-sensitive materials after the desired structures have been produced. The hardened structures are then separated from the surrounding, non-exposed material. “In this way, the perfect probe can be produced for any sample to be studied,” Hölscher explains.
Use of this process for enhancing atomic force microscopy is reported by the researchers in the Applied Physics Letters journal under the heading “Tailored probes for atomic force microscopy fabricated by two-photon polymerization”. The probes that can be produced in any shape can be placed on conventional, commercially available measurement needles and are hardly subject to wear. They are perfectly suited for studying biological samples, but also technical and optical components in the range od nanometers.
###
Research was financed by the German Research Foundation, a Starting Grant and a Senior Grant of the European Research Council (ERC), funds of the Alfried Krupp von Bohlen and Halbach Foundation, and the Federal Ministry of Education and Research under the PHOIBOS project. In addition, work was supported by the “Karlsruhe Nano-Micro Facility” (KNMF) of KIT.
Gerald Göring, Philipp-Immanuel Dietrich, Matthias Blaicher, Swati Sharma, Jan G. Korvink, Thomas Schimmel, Christian Koos, and Hendrik Hölscher: Tailored probes for atomic force microscopy fabricated by two-photon polymerization. Applied Physics Letters. DOI 10.1063/1.4960386.
For further information, please contact: Kosta Schinarakis, PKM – Science Scout, Phone: +49 721 608 41956, Fax: +49 721 608 43658, E-mail: schinarakis@kit.edu
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) pools its three core tasks of research, higher education, and innovation in a mission. With about 9,300 employees and 25,000 students, KIT is one of the big institutions of research and higher education in natural sciences and engineering in Europe.
KIT – The Research University in the Helmholtz Association
Since 2010, the KIT has been certified as a family-friendly university.
This press release is available on the internet at http://www.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…


