Taking correlated quantum Hall physics to the third dimension
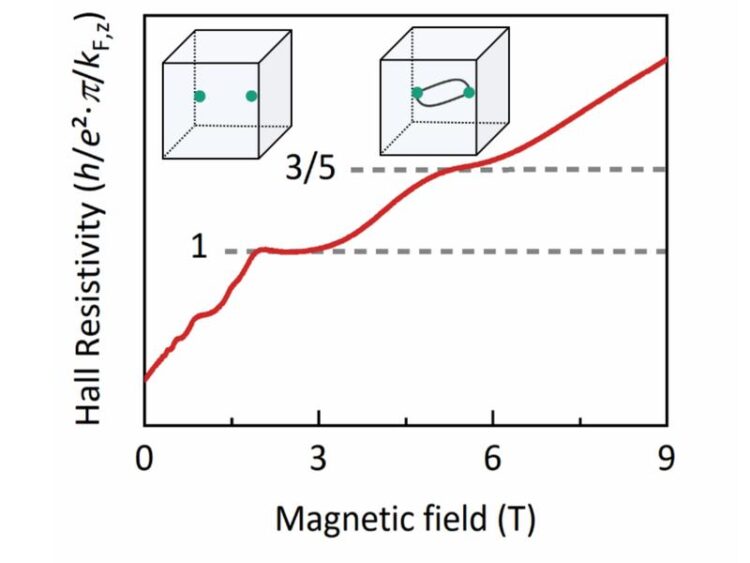
Hall resistivity as a function of magnetic field at 2 K in units of the Planck constant h, the elementary charge e and the Fermi wavevector along the magnetic field kF,z.
© MPI CPfS
Scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Physics of Solids and their international colleagues found signatures of an unconventional Hall response in the quantum limit of the bulk metal HfTe5, adjacent to the three-dimensional quantum Hall effect of a single electron band at low magnetic fields.
The quantum Hall effect is among the most prominent examples of a quantum phenomenon that occurs on a truly macroscopic scale. Its robust nature renders the quantum Hall effect vastly important for applications. It is nowadays for example used as the “gold standard” to gauge electric resistances. Even more importantly, the quantum Hall effect can be considered a drosophila for topological physics, and numerous topological states of matter can be understood building on the fundamental insights gained in connection to the quantum Hall effects over the past decades.
Traditionally, the quantum Hall effect has exclusive been associated with two-dimensional metals. Now, scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Physics of Solids in Dresden, the Technische Universität Dresden, the Brookhaven National Laboratory at New York, the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf, the University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the Wuerzburg-Dresden Cluster of Excellence ct.qmat have discovered a new strongly correlated electronic state in a three-dimensional metal that is a close relative of the two-dimensional quantum Hall state.
The team found signatures of an unconventional Hall response in the quantum limit of the bulk metal HfTe5, adjacent to the three-dimensional quantum Hall effect of a single electron band at low magnetic fields. The additional plateau-like feature in the Hall conductivity of the lowest Landau level is accompanied by a Shubnikov-de Haas minimum in the longitudinal electrical resistivity and its magnitude relates as 3/5 to the height of the last plateau of the three-dimensional quantum Hall effect. The findings are consistent with strong electron-electron interactions stabilizing an unconventional variant of the Hall effect in a three-dimensional material in the quantum limit.
Given that topological states of matter have been of utmost importance in our understanding of two-dimensional systems, these new findings promise exciting future insights. Examining the novel properties of quantum Hall physics in three-dimensional metals could not only allow scientists to better understand how far the mysterious realm of quantum Hall physics spreads, but also drive research on strongly correlated topological states in three-dimensional materials in general.
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Johannes.Gooth@cpfs.mpg.de
Originalpublikation:
S. Galeski, X. Zhao, R. Wawrzyńczak, T. Meng, T. Förster, P. M. Lozano, S. Honnali, N. Lamba, T. Ehmcke, Q. Li, G. Gu, W. Zhu, J. Wosnitza, C. Felser, G. F. Chen, J. Gooth. Unconventional Hall response in the quantum limit of HfTe5,
Nature Communications 11, 5926 (2020).
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-19773-y
Weitere Informationen:
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Largest magnetic anisotropy of a molecule measured at BESSY II
At the Berlin synchrotron radiation source BESSY II, the largest magnetic anisotropy of a single molecule ever measured experimentally has been determined. The larger this anisotropy is, the better a…

Breaking boundaries: Researchers isolate quantum coherence in classical light systems
LSU quantum researchers uncover hidden quantum behaviors within classical light, which could make quantum technologies robust. Understanding the boundary between classical and quantum physics has long been a central question…

MRI-first strategy for prostate cancer detection proves to be safe
Active monitoring is a sufficiently safe option when prostate MRI findings are negative. There are several strategies for the early detection of prostate cancer. The first step is often a…



