The importance of good neighbors in catalysis
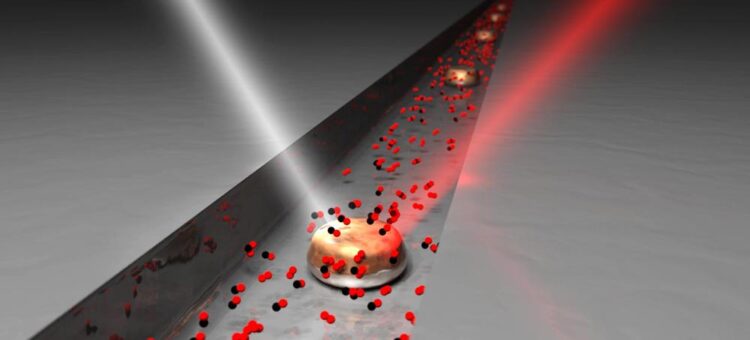
Neighbourly collaboration for catalysis. First, a number of nanoparticles of copper are isolated in a gas-filled nanotube. Researchers then use light to measure how they affect each other in the process by which oxygen and carbon monoxide become carbon dioxide. The long-term goal of the research is to find a resource-efficient "neighbourhood collaboration" where as many particles as possible are catalytically active at the same time.
Credit: David Albinsson/Chalmers University of Technology
Are you affected by your neighbours? So are nanoparticles in catalysts. New research from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, published in the journals Science Advances and Nature Communications, reveals how the nearest neighbours determine how well nanoparticles work in a catalyst.
“The long-term goal of the research is to be able to identify ‘super-particles’, to contribute to more efficient catalysts in the future. To utilise the resources better than today, we also want as many particles as possible to be actively participating in the catalytic reaction at the same time,” says research leader Christoph Langhammer at the Department of Physics at Chalmers University of Technology.
Imagine a large group of neighbours gathered together to clean a communal courtyard. They set about their work, each contributing to the group effort. The only problem is that not everyone is equally active. While some work hard and efficiently, others stroll around, chatting and drinking coffee. If you only looked at the end result, it would be difficult to know who worked the most, and who simply relaxed. To determine that, you would need to monitor each person throughout the day. The same applies to the activity of metallic nanoparticles in a catalyst.
The hunt for more effective catalysts through neighbourly cooperation
Inside a catalyst several particles affect how effective the reactions are. Some of the particles in the crowd are effective, while others are inactive. But the particles are often hidden within different ‘pores’, much like in a sponge, and are therefore difficult to study.
To be able to see what is really happening inside a catalyst pore, the researchers from Chalmers University of Technology isolated a handful of copper particles in a transparent glass nanotube. When several are gathered together in the small gas-filled pipe, it becomes possible to study which particles do what, and when, in real conditions.
What happens in the tube is that the particles come into contact with an inflowing gas mixture of oxygen and carbon monoxide. When these substances react with each other on the surface of the copper particles, carbon dioxide is formed. It is the same reaction that happens when exhaust gases are purified in a car’s catalytic converter, except there particles of platinum, palladium and rhodium are often used to break down toxic carbon monoxide, instead of copper. But these metals are expensive and scarce, so researchers are looking for more resource-efficient alternatives.
“Copper can be an interesting candidate for oxidising carbon monoxide. The challenge is that copper has a tendency to change itself during the reaction, and we need to be able to measure what oxidation state a copper particle has when it is most active inside the catalyst. With our nanoreactor, which mimics a pore inside a real catalyst, this will now be possible,” says David Albinsson, Postdoctoral researcher at the Department of Physics at Chalmers and first author of two scientific articles recently published in Science Advances and Nature Communications.
Anyone who has seen an old copper rooftop or statue will recognise how the reddish-brown metal soon turns green after contact with the air and pollutants. A similar thing happens with the copper particles in the catalysts. It is therefore important to get them to work together in an effective way.
“What we have shown now is that the oxidation state of a particle can be dynamically affected by its nearest neighbours during the reaction. The hope therefore is that eventually we can save resources with the help of optimised neighbourly cooperation in a catalyst,” says Christoph Langhammer, Professor at the Department of Physics at Chalmers.
###
More about the scientific publications:
* The article “Copper catalysis at operating conditions — bridging the gap between single nanoparticle probing and catalyst bed averaging” is written by David Albinsson, Astrid Boje, Sara Nilsson, Christopher Tiburski, Anders Hellman, Henrik Ström and Christoph Langhammer and was recently published in the scientific journal Nature Communications. The researchers are active at the Department of Physics and the Department of Mechanics and Maritime Sciences at Chalmers, as well as at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology, NTNU) in Trondheim, Norway.
https:/
* The article “Operando detection of single nanoparticle activity dynamics inside a model pore catalyst material” is written by David Albinsson, Stephan Bartling, Sara Nilsson, Henrik Ström, Joachim Fritzsche and Christoph Langhammer, and has been published in the scientific journal Science Advances. The researchers are active at the Department of Physics and the Department of Mechanics and Maritime Sciences at Chalmers University of Technology, as well as at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology, NTNU) in Trondheim, Norway.
https:/
For more information contact:
David Albinsson, Postdoctoral researcher, Department of Physics, Chalmers, +46 31 772 54 21, aldavid@chalmers.se
Christoph Langhammer, Professor, Department of Physics, Chalmers, +46 31 772 33 31, clangham@chalmers.se
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



