Two photons strongly coupled by glass fiber
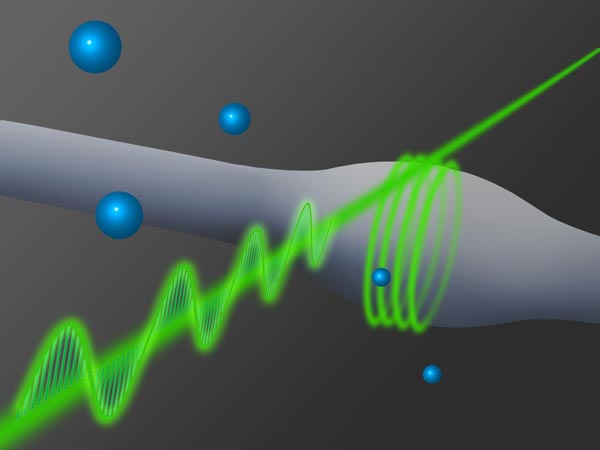
The light in a glass fiber is coupled to a bottle resonator. Credit: TU Wien
Two photons in free space do not interact. Light waves can pass through each other without having any influence on each other at all. For many applications in quantum technology, however, interaction between photons is crucial.
It is an indispensable prerequisite for transmitting information through tap-proof quantum channels or for building optical logic gates. At the Vienna University of Technology (TU Wien), scientists have now succeeded in establishing a strong interaction between two single photons. This opens up completely new possibilities for quantum optics. The experimental results have now been published in the journal “Nature Photonics”.
Interaction Usually Requires Bright Light
“In order to have light interact with light, people have been using so-called nonlinear media”, says Professor Arno Rauschenbeutel (Institute for Atomic and Subatomic Physics, TU Wien). The light has an effect on the properties of these materials, and the material in turn influences the light, which leads to an indirect coupling between photons. This technique, however, can only be used at strong light intensities, when countless photons are involved.
At TU Wien, a system was built which creates a strong interaction between only two photons. This interaction is so strong that the phase of the photons is changed by 180 degrees. “It is like a pendulum, which should actually swing to the left, but due to coupling with a second pendulum, it swings to the right. There cannot be a more extreme change in the pendulum's oscillation”, says Rauschenbeutel. “We achieve the strongest possible interaction with the smallest possible intensity of light.”
A Photon in a Bottle
To make this possible, the photon has to be sent on an unlikely journey. An ultra-thin glass fibre is coupled to a tiny bottle-like light resonator so that light can partly enter the resonator, move in circles and return to the glass fibre. This detour through the resonator leads to the phase of the photon being inverted: a wave crest appears where a wave trough would have been expected.
When, however, a single rubidium atom is coupled to the resonator, the system is changed dramatically. Due to the presence of the atom, hardly any light enters the resonator anymore and the oscillation phase of the photon cannot be inverted.
Two Photons at Once
Things change when two photons arrive at the same time. “The atom is an absorber which can be saturated”, says Arno Rauschenbeutel. “A photon is absorbed by the atom for a short while and then released into the resonator. During that time, it cannot absorb any other photons. If two photons arrive simultaneously, only one can be absorbed, while the other can still be phase shifted.”
From a quantum mechanical point of view, there is no difference between the two photons. They can only be understood as a joint wave-like object, which is located in the resonator and in the glass fibre at the same time. The photons are indistinguishable. No one can tell which of them is being absorbed and which one has passed. When both hit the resonator at the same time, both of them together experience a phase shift by 180 degrees. Two interacting photons arriving simultaneously show a completely different behaviour than single photons.
The Building Blocks of Future Quantum Data-Highways?
“That way, a maximally entangled photon state can be created”, says Arno Rauschenbeutel. “Such states are required in all fields of quantum optics – in quantum teleportation, or for light-transistors which could potentially be used for quantum computing.”
A big advantage of the new system is that it is based on glass fibre technology, which is already being used for online communication anyway. Nano glass fibres and bottle-resonators are perfectly compatible with existing technologies. The targeted creation of a strong photon-photon-interaction is an important step towards a worldwide quantum information network for the tap-proof transmission of data.
Further information:
Prof. Arno Rauschenbeutel
Insitute for Atomic and Subatomic Physics
Vienna Center for Quantum Science and Technology
TU Wien
Stadionallee 2, 1020 Wien
T: +43-1-58801-141761
arno.rauschenbeutel@tuwien.ac.at
Dr. Jürgen Volz
Insitute for Atomic and Subatomic Physics
Vienna Center for Quantum Science and Technology
TU Wien
Stadionallee 2, 1020 Wien
T: +43-1-58801-141739
juergen.volz@tuwien.ac.at
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.tuwien.ac.at/tu_vienna/All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…


