Ultracold quantum mix
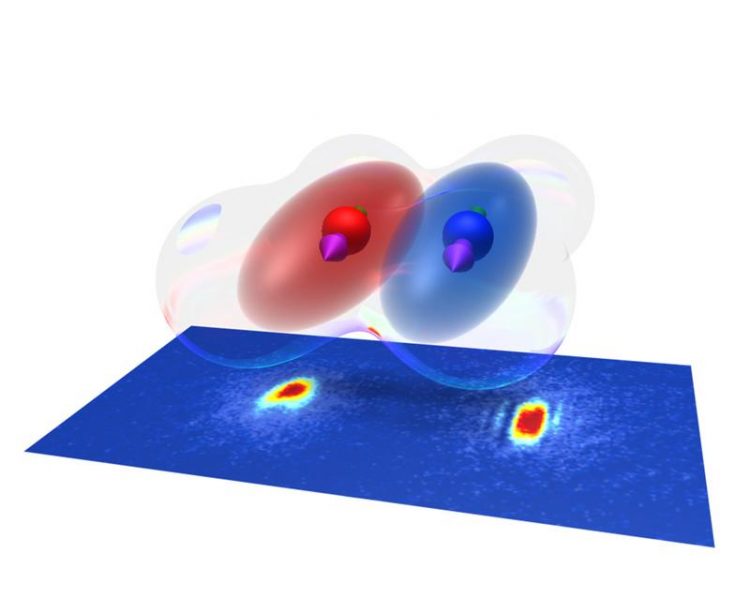
The Bose-Einstein condensates of Erbium and Dysprosium coexist and interact with each other. IQOQI Innsbruck
Only a few years ago it seemed unfeasible to extend the techniques of atom manipulation and deep cooling in the ultracold regime to many-valence-electron atomic species. The reason being the increasing complexity in the atomic spectrum and the unknown scattering properties.
However, a team of researchers, led by Ben Lev, in the US at Stanford University and an Austrian team, directed by Francesca Ferlaino, at the University of Innsbruck took the challenge and demonstrated quantum degeneracy of rare-earth species, using the strongly-magnetic, and rather unexplored, Dysprosium and Erbium atoms.
Ferlaino’s group focused the research on Erbium and developed a powerful, yet surprisingly simple approach to produce a Bose-Einstein condensate. “We have shown how the complexity of atomic physics can open up new possibilities,” says Francesca Ferlaino from the Department of Experimental Physics at the University of Innsbruck and the Institute of Quantum Optics and Quantum Information (IQOQI) at the Austrian Academy of Sciences.
Research on magnetic species is gathering momentum worldwide since such atoms proved to be an ideal platform to create dipolar quantum matter, in which particles interact with each other via a long-range and orientation dependent interaction as little quantum magnets.
Dipolar quantum matter
In a new paper now published in the journal Physical Review Letters, the Austrian research team makes a new leap in the field of dipolar matter. They have mixed Erbium and Dysprosium and for the first time produced a dipolar quantum mixture.
“We studied very carefully the atomic spectra of these two species and made plans on how to combine them and reach simultaneous quantum degeneracy”, says Philipp Ilzhöfer, one of the two leading authors of the paper, “and our scheme worked out even better than expected allowing us to create a system in which Bose-Einstein condensates of Erbium and Dysprosium coexist and interact with each other”, adds Arno Trautmann, the other leading author. This advance promises to open novel research frontiers in the field of dipolar quantum matter because of the long-range interaction among the two species.
The research has been conducted in a new laboratory at the IQOQI and has been supported by the Austrian Academy of Sciences and an ERC Consolidator Grant. The work has been recommended by the editors of the journal as particularly important, interesting, and well written.
Francesca Ferlaino
Institute for Quantum Optics and Quantum Information
Austrian Academy of Sciences
Phone: +43 512 507 4740
Email: francesca.ferlaino@oeaw.ac.at
Web: http://www.erbium.at
Dipolar Quantum Mixtures of Erbium and Dysprosium Atoms. A. Trautmann, P. Ilzhöfer, G. Durastante, C. Politi, M. Sohmen, M. J. Mark, and F. Ferlaino. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.213601
https://physics.aps.org/synopsis-for/10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.213601 – Physics Synopsis: Making Mixtures of Magnetic Condensates
http://www.erbium.at – Arbeitsgruppe Dipolar Quantum Gases (Francesca Ferlaino)
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uibk.ac.atAll latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

An Endless Loop: How Some Bacteria Evolve Along With the Seasons
The longest natural metagenome time series ever collected, with microbes, reveals a startling evolutionary pattern on repeat. A Microbial “Groundhog Year” in Lake Mendota Like Bill Murray in the movie…

Witness Groundbreaking Research on Achilles Tendon Recovery
Achilles tendon injuries are common but challenging to monitor during recovery due to the limitations of current imaging techniques. Researchers, led by Associate Professor Zeng Nan from the International Graduate…

Why Prevention Is Better Than Cure—A Novel Approach to Infectious Disease Outbreaks
Researchers have come up with a new way to identify more infectious variants of viruses or bacteria that start spreading in humans – including those causing flu, COVID, whooping cough…



