Ultrasonic measurement technology of the future
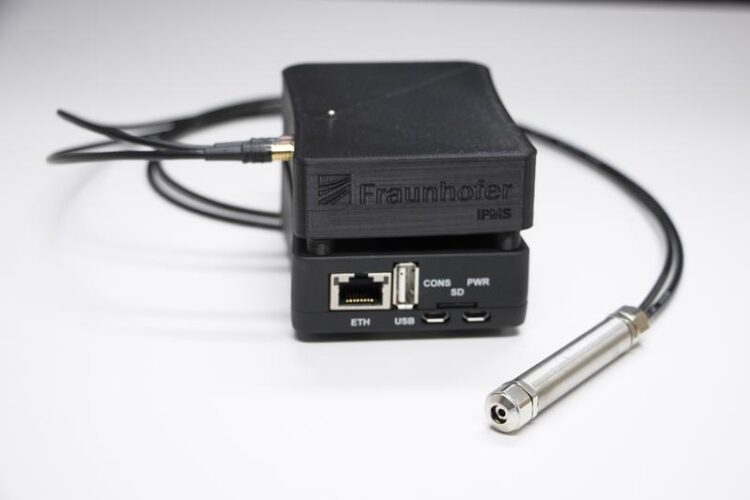

Customer Evaluation Kit for CMUT ultrasound sensors of Fraunhofer IPMS.
Image: Fraunhofer IPMS
The Fraunhofer Institute for Photonic Microsystems IPMS in Dresden has been developing robust, reliable and versatile ultrasonic sensors for many years. Due to their small size, the so-called MUTs, Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducers, enable energy-saving, multifunctional, environmentally friendly and extremely compact sensor systems. At the digital trade fair SENSOR+TEST, the world’s leading forum for sensor, measurement and testing technology, which is free of charge for visitors, the institute will present its latest developments to the public from May 4 – 6, 2021.
Image: Fraunhofer IPMS
Nowadays, ultrasonic sensors are fully integrated into everyday life. They support the driver as parking assistance in automobiles, ensure safety when humans and robots work together, secure filling levels and material flow in the beverage and food industry, or serve as imaging methods for the examination of embryos or organic tissue in medicine. This versatility is made possible by the propagation and detection of high-frequency sound pulses that are inaudible to humans. These ensure non-contact, reliable and accurate detection of objects for a wide variety of materials regardless of aggregate state, shape and color under almost any circumstances and in virtually any environment.
The micromachined ultrasonic transducers (MUT) developed by Fraunhofer IPMS are based on micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) and are key to the miniaturization of components and devices without which no high-growth technical sector could survive. “Our miniaturized capacitive miromachined ultrasonic transducers (CMUT) benefit from reliable manufacturing processes in CMOS technology. This enables cost-effective and RoHS-compliant production in high volumes. This is not the case with classic piezoelectric ultrasonic sensors, which are manufactured in a complex precision mechanical process and often contain lead,” explains Dr. Sandro Koch, scientist at Fraunhofer IPMS. The sensors can be manufactured for a wide range of ultrasonic frequencies, so that application-specific ranges and resolutions are possible. Sensor solutions can be manufactured in single-channel structures as well as in any two-dimensional array structures. The latter enable, for example, the application of imaging methods for environmental monitoring and are thus pioneering in safe human-robot collaboration.
In order to provide interested parties with a quick introduction to the innovative sensor technologies of Fraunhofer IPMS, the institute offers an evaluation kit. It consists of either one or two CMUT sensor modules, adapted control electronics, and software as a web application that controls the ultrasonic sensor via plug-and-play. In the specific working range, the system is able to send or receive ultrasonic signals with high sensitivity and resolution. The system transmits the data to the web application via Ethernet or Wifi, enabling simultaneous visualization. Users can thus convince themselves of the technical advantages of Fraunhofer IPMS’ CMUT technology with little effort and evaluate this sensor technology for various application scenarios – such as close-range monitoring, acoustic spectroscopy, flow measurement – in which there is a need for miniaturization with simultaneously increased sensitivity.
One of the latest developments of Fraunhofer IPMS is the Nanoscopic Electrostatic Drive (NED) MEMS ultrasonic transducer. This technology makes it possible to dispense with the membrane used in conventional ultrasound transducers. Instead, microscopic bending beams are used, which are set in vibration by a signal. To generate sound, these bending beams are arranged in sound chambers. Sound exits the sound chambers through inlet and outlet slits. The advantages of this system are very low power requirements and RoHS compatibility, as well as a high number of degrees of freedom in design.
At Sensor+Test’s accompanying conference, Sensor Measurement and Science International (SMSI), Jorge Mario Monsalve Guaracao, scientist at Fraunhofer IPMS, will present a micromechanical ultrasonic transducer (MUT), which is used, for example, in the field of gesture recognition.
Visitors can register for the free digital trade fair Sensor+Test via the organizer’s website at: https://www.sensor-test.de/sensor-test-2021-for-visitors/exhibition-ticket/
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Dr. Sandro Koch, sandro.koch@ipms.fraunhofer.de
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…


