Upgraded code reveals a source of damaging fusion disruptions
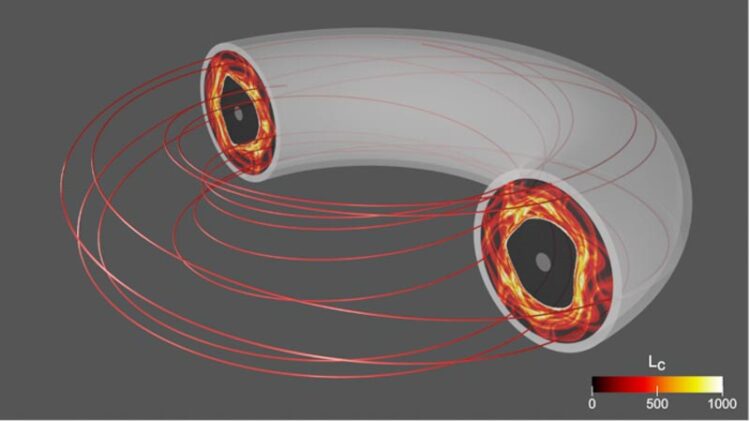
Destructive magnetic perturbations create a complex 3-D structure of magnetic field lines that randomly wander inside the tokamak. The red line shows the 3-D trajectory of an example field line, and each field line can have a significantly different trajectory. The colors of the cross-section represent the length of field line trajectory through each area, from short (black) to long (yellow) lengths.
Credit: Min-Gu Yoo
Discoveries reveal an escape route for high-energy electrons that can lead to thermal quenches.
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) and Los Alamos National Laboratory have uncovered a key process behind a major challenge called thermal quenches, the rapid heat loss in hot plasmas that can occur in doughnut-shaped tokamak fusion devices. Such quenches are sudden drops of electron heat in the plasma that fuels fusion reactions, drops that can create damaging disruptions inside the tokamak. Understanding the physics behind these quenches, caused by powerful perturbations in the magnetic fields that confine the plasma in tokamaks, could lead to methods to mitigate or prevent them.
Researchers have now traced a comprehensive mechanism for thermal quenches to turbulent particle transport. Using the laboratory’s Gyrokinetic Tokamak Simulation (GTS) code, the physicists explored how the hot plasma, which is composed of free electrons and atomic nuclei, or ions, generates the electric field and the turbulent particle transport at the outset of quenches.
The GTS code was originally developed at PPPL to simulate turbulence and transport physics in the hot core plasmas which are confined by magnetic fields in tokamaks. Recently, the GTS code has been extended to study more complex plasmas and magnetic fields, such as destructive magnetic perturbations that break the magnetic field cage and create chaotic 3-D magnetic field lines (Figure 1). The introduction of novel numerical algorithms and the acceleration of graphics processing units made this powerful new capability possible. This upgrade enables the consistent simulation of plasma transport during thermal quenches at lower computational costs, yielding important new insights into disruption physics.
The GTS code traced the plasma transport mechanism to the evolution of a self-generated electric field in 3-D chaotic magnetic fields, whose complexity had previously made the quenching mechanisms difficult to understand. The improved code unraveled the controversy and laid bare the physics behind the mechanism.
The self-generated field mixes up the plasma, causing high-energy electrons to escape from the core and fly toward the wall. This enhanced heat transport produces a rapid and continuous drop in electron temperature, leading to the thermal quench.
From the simulation results and comparison to experimental observations, researchers found that this novel mechanism could be a major contributor to the abrupt quenches. The researchers have proposed an analytic model of plasma transport that provides new physical insights for understanding the complex topology of 3-D magnetic field lines. These breakthrough discoveries could lead to new steps to battle damaging disruptions.
Abstract
TI02.00001 Collisonless transport mechanisms for thermal quench in stochastic magnetic fields open at the wall boundary
Session
TI02: MFE IV: Edge and Scrape-Off Layer Plasmas
9:30 AM–12:30 PM, Thursday, November 11, 2021
Room: Ballroom C
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…


