You can hear every event twice in a three-dimensional quantum gas
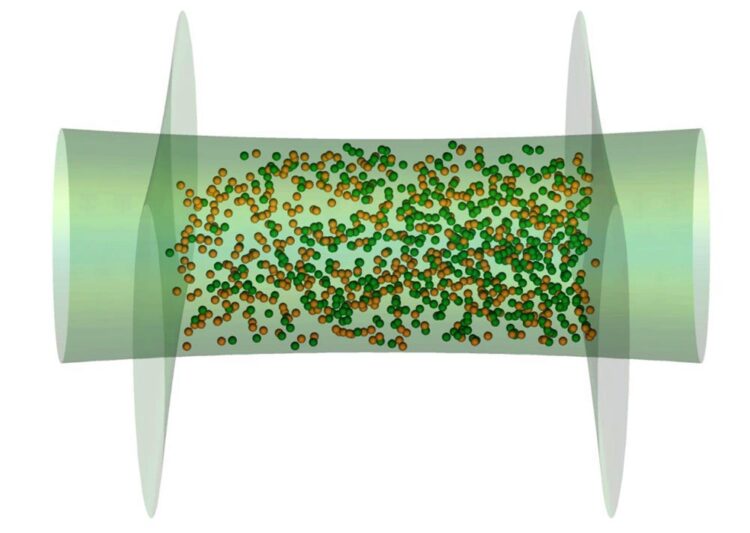
The image depicts the optical box trap, made of green laser light shaped into a tube and two light sheets, with the partially condensed gas held inside. The superfluid component, mainly consisting of the condensate, is represented as coloured in green and is oscillating to the side, decoupled from the normal component coloured orange.
Image Credit: Lena Hannah Dogra
You heard it here first, and then again.
If you could immerse yourself in a quantum fluid, you would hear every event twice, because they support two sound waves with different speeds.
The researchers in their experiment have realized this remarkable property for the first time in a three-dimensional quantum gas, instead of a quantum liquid. They achieved this result through cooling a gas of potassium atoms trapped by laser beams in ultrahigh vacuum to less than a millionth of a degree above absolute zero temperature, where it partly forms a Bose-Einstein Condensate.
Those are typically weakly interacting, but in their experiment, they increase the interaction so much that the gas becomes hydrodynamic. They excite standing waves at different frequencies and observe two resonances of so-called first and second sound.
This effect is well studied in quantum liquids like superfluid helium, but the compressibility of their Bose gas is as large as the one of air, so it is still a gas, not a liquid. Remarkably, Landau’s famous two-fluid model, a theory developed for superfluid helium in the 1940s, still describes their superfluid gas well. In their system, the two fluids mainly consist of the condensed and non-condensed parts of the gas respectively.
They experimentally resolve the relative motion of the two parts, which oscillate together in the classical first sound but move opposite to each other in second sound. The microscopic theoretical description of their gas is much simpler than the one for a liquid, promising new insights into the understanding of quantum hydrodynamics.
To read the research paper, click here.
Journal: Physical Review Letters
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.128.223601
Media Contact
Pooja Pandey
University of Cambridge
pp550@cam.ac.uk
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…


