A rethink of the building blocks for solar panels could help mass production
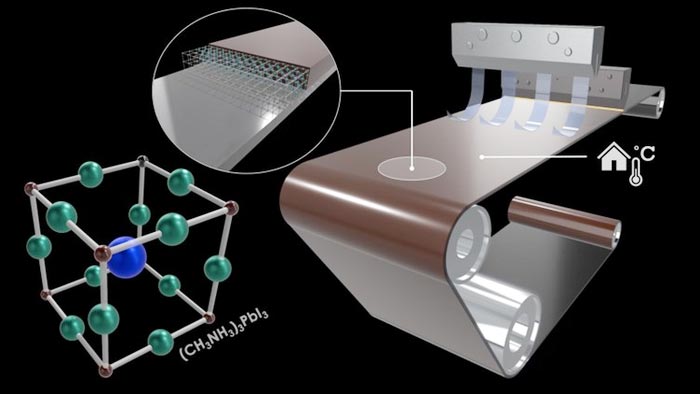
A route towards the fabrication of large-scale and high-quality perovskite films for optoelectronic devices
Credit: University of Surrey/ Advanced Technology Institute
An original approach to mass-producing low-cost solar cell foundation blocks could lead to the wide adoption of solar panels made from perovskite ink – a “miracle material” – according to research from the University of Surrey.
In the paper published in Scientific Reports, Dr Ehsan Rezaee, a post-doctoral fellow of the Advanced Technology Institute (ATI) at the University of Surrey, explains his research:
“The objective is simply to produce solar cell building blocks out of perovskite ink. Whilst perovskite ink is not a new technology, current inks do not guarantee seamless transitions on an industrial scale, as the manufacturing process needs to be highly controlled and optimised.
“Our perovskite ink produces a fast and reproducible way to reliably fabricate these solar cell building blocks on a mass scale, paving the way for its use in commercial markets.”
Perovskite solar cells are a low-cost, lightweight solution and can be built either rigid or flexible, with more possibilities to easily transport and install. The new study examines the foundation blocks of solar cells made of perovskite rather than the traditional silicon, as perovskite cells harvest light through the visible part of the solar spectrum, which has more energy.
Professor Ravi Silva, Director of the ATI at the University of Surrey, said:
“The University of Surrey has always believed in the potential of solar panels to be a critical research area which will, in time, allow us to move away from dangerous old energy sources.
“However, we must do more to improve the connection between research and production on a mass industry scale in order to see this as a future turning point, which is the purpose of our paper.”
The University of Surrey is a leading research institution that focuses on sustainability for the benefit of society to deal with the many challenges of climate change. It is also committed to improving its own resource efficiency on its own estate in Guildford and being a sector leader. It has set a commitment to be carbon neutral by 2030. In April, it was ranked 55th in the world by the Times Higher Education (THE) University Impact Rankings which assesses more than 1,400 universities’ performance against the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
The work can be found here https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-10790-z
[Ends]
Notes to Editors
- Dr Ehsan Rezaee and Professor Ravi Silva are available for interview upon request.
- Contact the University of Surrey media team via mediarelations@surrey.ac.uk
Journal: Scientific Reports
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-10790-z
Article Title: A route towards the fabrication of large-scale and high-quality perovskite films for optoelectronic devices
Article Publication Date: 6-May-2022
Media Contact
Katherine Ingram
University of Surrey
k.ingram@surrey.ac.uk
Cell: 7537828242
Original Source
All latest news from the category: Power and Electrical Engineering
This topic covers issues related to energy generation, conversion, transportation and consumption and how the industry is addressing the challenge of energy efficiency in general.
innovations-report provides in-depth and informative reports and articles on subjects ranging from wind energy, fuel cell technology, solar energy, geothermal energy, petroleum, gas, nuclear engineering, alternative energy and energy efficiency to fusion, hydrogen and superconductor technologies.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



