A simple, yet versatile, new design for chaotic oscillating circuitry inspired by prime numbers
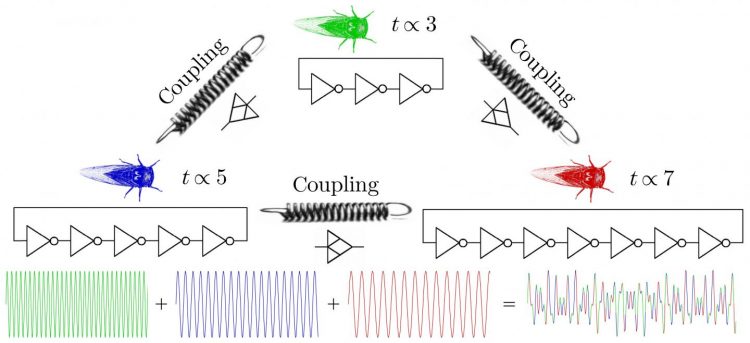
The simple idea underlying the design of the circuit is linking together some ring oscillators having lengths equal to the smallest odd prime numbers, such as 3, 5 and 7 (top). Even a simple sum between sine waves having such periods yields a complicated-looking signal (bottom), but the interactions between real oscillators lead to a much richer scenario. Credit: Ludovico Minati
Our ability to recreate the signals found in natural systems, such as those in brains, swarms, and the weather, is useful for our understanding of the underlying principles. These signals can be very complex, to the extreme case of the so-called “chaotic signals.”
Chaos does not mean randomness; it represents a very complicated type of order. Minute changes in the parameters of a chaotic system can result in greatly different behaviors. Chaotic signals are difficult to predict, but they are present in lots of different scenarios.
Unfortunately, the generation of chaotic signals with desired features is a difficult task. Creating them digitally is in some cases too power consuming, and approaches based on analog circuits are necessary. Now, researchers in Japan, Italy, and Poland propose a new approach for creating integrated circuits that can generate chaotic signals.
This research was the result of a collaboration between scientists from Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), in part funded by the World Research Hub Initiative, the Universities of Catania and Trento, Italy, and the Polish Academy of Sciences in Krakow, Poland.
The research team started from the idea that cycles that have periods set by different prime numbers cannot develop a fixed phase relationship. Surprisingly, this principle seems to have emerged in the evolution of several species of cicadas, whose life cycles follow prime numbers of years, to avoid synchronizing with each other and with predators.
For example, if one tries to “tie together” oscillators with periods set to the first three prime numbers (3, 5 and 7), the resulting signals are very complicated and chaos can readily be generated (Fig. 1).
The design started from the most traditional oscillator found in integrated circuits, called the “ring oscillator,” which is small and does not require reactive components (capacitors and inductors). Such a circuit was modified so that the strengths of ring oscillators having three, five and seven stages could be controlled independently, along with the tightness of their linkages.
The device could generate chaotic signals over a wide frequency spectrum, from audible frequencies to the radio band (1 kHz to 10 MHz). “Moreover, it could do so at a rather low power consumption, below one-millionth of a watt,” explains Dr. Hiroyuki Ito, head of the laboratory where the prototype was designed.
Even more remarkable was the discovery that totally different types of signals could be generated depending on the slightly different characteristics the individual prototypes (Fig. 2). For example, the researchers recorded trains of spikes quite similar to what is found in biological neurons.
They also found situations in which the rings “fought each other” to the point of almost completely suppressing their activity: this phenomenon is called “oscillation death.”
“This circuit draws its beauty from a really essential shape and principle, and simplicity is key to realizing large systems operating collectively in a harmonious manner, especially when it enriched by small differences and imperfections, such as those found in the realized circuits,” says Dr. Ludovico Minati, lead author of the study.
The team believes in its future ability to be a building block for many different applications. They will work on integrating this circuit with sensors to, for example, measure chemical properties in the soil. Additionally, they will create networks of these oscillators on single computer chips interconnected in manners that resemble biological neural circuits. They hope to realize certain operations while consuming many times less power than a traditional computer.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.291290All latest news from the category: Power and Electrical Engineering
This topic covers issues related to energy generation, conversion, transportation and consumption and how the industry is addressing the challenge of energy efficiency in general.
innovations-report provides in-depth and informative reports and articles on subjects ranging from wind energy, fuel cell technology, solar energy, geothermal energy, petroleum, gas, nuclear engineering, alternative energy and energy efficiency to fusion, hydrogen and superconductor technologies.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



