Engineers invent ultra-fast manufacturing technology, eliminating need for polymer binders
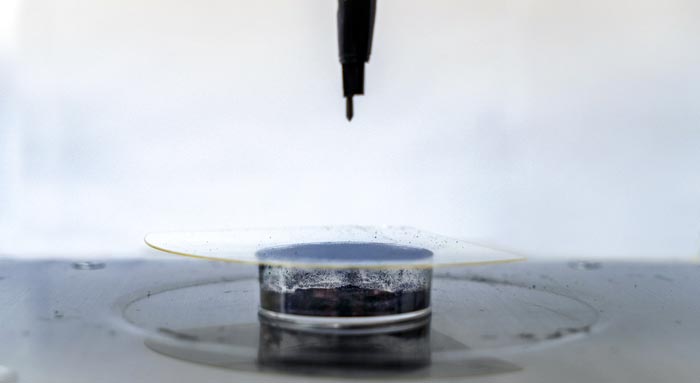
Corona-Enabled Electrostatic Printing prints electronic skin, or “e-skin,” by using corona discharge to create a strong electric field between binder-free functional powders, such as graphene, and flexible, non-conductive surfaces, such as medical tape. The electrostatic force enables a multitude of e-skin sensors to be printed within sub-seconds, compared to the 20 minutes it takes with polymer binders, and doesn’t require heat.
Credit: University of South Florida
A team of engineers at the University of South Florida has invented new technology that could forever change the manufacturing of wearable, electronic sensors. They’ve figured out a way to speed up production without having to use polymer binders – the industry standard in printing flexible sensors, which are often used to monitor vital signs in health care settings.
Their technology, featured on the cover of the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, prints electronic skin, or “e-skin,” by using corona discharge to create a strong electric field between binder-free functional powders, such as graphene, and flexible, non-conductive surfaces, such as medical tape. The electrostatic force used in Corona-Enabled Electrostatic Printing enables a multitude of e-skin sensors to be printed within sub-seconds, compared to the 20 minutes it takes with polymer binders, and doesn’t require heat. E-skin is micrometer-thin, pliable technology that can be used to measure things such as strain, temperature and sound.
Ying Zhong, assistant professor of mechanical engineering at USF, and her collaborator, Long Wang at California Polytechnic State University, found that the printing technique has broad applications, such as in health monitoring, prosthetics and robotics. Unlike with polymer binders, there aren’t sizing limitations, making the technique a strong candidate for the roll-to-roll manufacturing of large flexible sensors, which can greatly reduce production costs.
“As a new, advanced manufacturing strategy, Corona-Enabled Electrostatic Printing will potentially transform the cost structure for large-area and high-performance electronics and enable versatile applications of flexible, functional systems,” Zhong said. “The technique can help contribute to maintaining the U.S.’s leadership in advanced manufacturing.”
Zhong recently received a $308,928 grant from the National Science Foundation to advance her research, proving the patent-pending ultra-fast manufacturing technique can be used to print materials beyond multifunctional e-skin.
About the University of South Florida
The University of South Florida is a high-impact global research university dedicated to student success. Over the past 10 years, no other public university in the country has risen faster in U.S. News and World Report’s national university rankings than USF. Serving more than 50,000 students on campuses in Tampa, St. Petersburg and Sarasota-Manatee, USF is designated as a Preeminent State Research University by the Florida Board of Governors, placing it in the most elite category among the state’s 12 public universities. USF has earned widespread national recognition for its success graduating under-represented minority and limited-income students at rates equal to or higher than white and higher income students. USF is a member of the American Athletic Conference.
Learn more at www.usf.edu
Journal: ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
Method of Research: Experimental study
Subject of Research: Not applicable
Article Title: Corona-Enabled Electrostatic Printing for Ultra-fast Manufacturing of Binder-Free Multifunctional E‐Skins
Media Contact
Tina Meketa
University of South Florida (USF Innovation)
tmeketa@usf.edu
Office: 813-955-2593
All latest news from the category: Power and Electrical Engineering
This topic covers issues related to energy generation, conversion, transportation and consumption and how the industry is addressing the challenge of energy efficiency in general.
innovations-report provides in-depth and informative reports and articles on subjects ranging from wind energy, fuel cell technology, solar energy, geothermal energy, petroleum, gas, nuclear engineering, alternative energy and energy efficiency to fusion, hydrogen and superconductor technologies.
Newest articles

Witness Groundbreaking Research on Achilles Tendon Recovery
Achilles tendon injuries are common but challenging to monitor during recovery due to the limitations of current imaging techniques. Researchers, led by Associate Professor Zeng Nan from the International Graduate…

Why Prevention Is Better Than Cure—A Novel Approach to Infectious Disease Outbreaks
Researchers have come up with a new way to identify more infectious variants of viruses or bacteria that start spreading in humans – including those causing flu, COVID, whooping cough…

Durable, Efficient, Sustainable: The Rise of Cerium Oxide Thermal Switches
Groundbreaking cerium oxide-based thermal switches achieve remarkable performance, transforming heat flow control with sustainable and efficient technology. Cerium Oxide-Based Thermal Switches Revolutionize Heat Flow Control Thermal switches, which electrically control…



