Let the sunshine in: self-cleaning membrane under visible light treatment
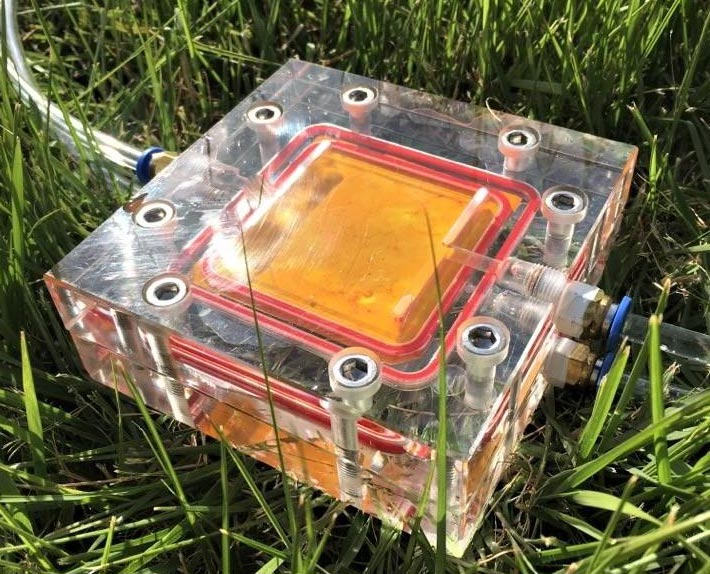
The hydrophilic photocatalytic membrane showed excellent antimicrobial activity under visible light and the anti-biofouling property enabled a complete flux recovery of the membrane in repeated cycles.
Credit: Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST)
Complete removal of microbial contaminant layer accumulated on the membrane surface by sunlight irradiation. Providing a foundation for the development of new membrane materials on the convergence between water treatment and photocatalyst technologies.
Membrane technology is widely used in various water treatment processes such as water desalination, sewage treatment, and advanced water treatment for producing clean tap water. The membrane filtration technology is a method that can significantly improve water quality and has been suggested as an alternative that can radically prevent larvae in the tap water that has become a widespread issue in Korea recently. However, the current membrane technology suffers from a rapid performance reduction due to the accumulation of bacterial adhesion on the membrane surface and the growth of microbial cells, leading to high maintenance costs.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) reported that the research team led by Dr. Jeehye Byun and Director Seok Won Hong from Water Cycle Research Center developed a membrane material that self-cleans biological contaminants through irradiation of sunlight. According to the team, the newly developed membrane material is expected to significantly reduce the cost of membrane management as the membrane can be reused after just 10 minutes of sunlight irradiation.
Water treatment membranes require periodic cleaning as the contaminants are accumulated on the membrane surface after water filtration. Currently, used membranes require to be cleaned with harsh chemicals for more than six hours at least once a week, which results in fairly high operating cost and damages the membranes due to the chemicals.
As a way to address these issues, the researchers at KIST firmly conjugated a visible-light-responsive photocatalyst to the water treatment membrane surface. This surface-modified photocatalytic membrane can fully decompose contaminants accumulated on the surface when irradiated with visible light, thereby easily cleaning the membrane. In particular, it displayed outstanding performance by removing 99.9% of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus, and viruses, such as MS2 bacteriophage, accumulated on the membrane surface in less than an hour of light treatment. According to the team, the developed membrane can treat not only microbial cells but also organic contaminants such as dye solutions and heavy metals. Further, it showed the advantage of maintaining performance even after repeating the tests more than 10 times.
“Our research revealed that the efficiency of the water treatment processes can be improved by conjugating the photocatalytic technology and the water treatment membrane technology,” Dr. Jeehye Byun from KIST said. “Based on these research results, we will endeavor to develop next-generation membranes that can lead the water treatment membrane market.”
###
This study was carried out with a grant from the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), as part of the Institutional R&D Program of KIST. The findings were reported in the latest edition of the international journal, Applied Catalysis B:Environmental (IF: 16.683, Top 0.943% in the field of JCR).
All latest news from the category: Power and Electrical Engineering
This topic covers issues related to energy generation, conversion, transportation and consumption and how the industry is addressing the challenge of energy efficiency in general.
innovations-report provides in-depth and informative reports and articles on subjects ranging from wind energy, fuel cell technology, solar energy, geothermal energy, petroleum, gas, nuclear engineering, alternative energy and energy efficiency to fusion, hydrogen and superconductor technologies.
Newest articles

Parallel Paths: Understanding Malaria Resistance in Chimpanzees and Humans
The closest relatives of humans adapt genetically to habitats and infections Survival of the Fittest: Genetic Adaptations Uncovered in Chimpanzees Görlitz, 10.01.2025. Chimpanzees have genetic adaptations that help them survive…

You are What You Eat—Stanford Study Links Fiber to Anti-Cancer Gene Modulation
The Fiber Gap: A Growing Concern in American Diets Fiber is well known to be an important part of a healthy diet, yet less than 10% of Americans eat the minimum recommended…

Trust Your Gut—RNA-Protein Discovery for Better Immunity
HIRI researchers uncover control mechanisms of polysaccharide utilization in Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. Researchers at the Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based Infection Research (HIRI) and the Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) in Würzburg have identified a…



