Scientists create biodegradable, paper-based biobatteries
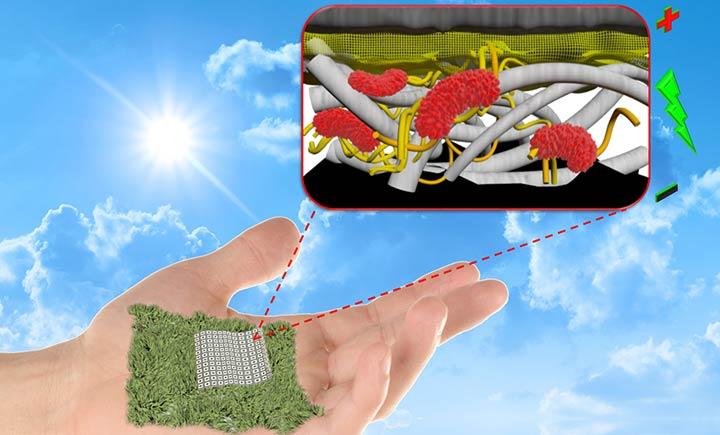
Researchers at Binghamton University, State University at New York have created a biodegradable, paper-based battery that is more efficient than previously possible. Credit: Seokheun 'Sean' Choi
The batteries of the future may be made out of paper. Researchers at Binghamton University, State University at New York have created a biodegradable, paper-based battery that is more efficient than previously possible.
For years, there has been excitement in the scientific community about the possibility of paper-based batteries as an eco-friendly alternative. However, the proposed designs were never quite powerful enough, they were difficult to produce and it was questionable whether they were really biodegradable.
This new design solves all of those problems.
Associate Professor Seokheun “Sean” Choi from the Electrical and Computer Engineering Department and Professor Omowunmi Sadik from the Chemistry Department worked on the project together. Choi engineered the design of the paper-based battery, while Sadik was able to make the battery a self-sustaining biobattery.
“There's been a dramatic increase in electronic waste and this may be an excellent way to start reducing that,” said Choi. “Our hybrid paper battery exhibited a much higher power-to-cost ratio than all previously reported paper-based microbial batteries.”
The biobattery uses a hybrid of paper and engineered polymers. The polymers – poly (amic) acid and poly (pyromellitic dianhydride-p-phenylenediamine) – were the key to giving the batteries biodegrading properties. The team tested the degradation of the battery in water and it clearly biodegraded without the requirements of special facilities, conditions or introduction of other microorganisms.
The polymer-paper structures are lightweight, low-cost and flexible. Choi said that flexibility also provides another benefit.
“Power enhancement can be potentially achieved by simply folding or stacking the hybrid, flexible paper-polymer devices,” said Choi.
The team said that producing the biobatteries is a fairly straightforward process and that the material allows for modifications depending on what configuration is needed.
###
The research paper, titled “Green Biobatteries: Hybrid Paper-Polymer Microbial Fuel Cells,” was published in Advanced Sustainable Systems.
The work was supported by a grant from the National Science Foundation and done through the Center for Research in Advanced Sensing Technologies and Environmental Sustainability (CREATES).
Media Contact
More Information:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/adsu.201800041All latest news from the category: Power and Electrical Engineering
This topic covers issues related to energy generation, conversion, transportation and consumption and how the industry is addressing the challenge of energy efficiency in general.
innovations-report provides in-depth and informative reports and articles on subjects ranging from wind energy, fuel cell technology, solar energy, geothermal energy, petroleum, gas, nuclear engineering, alternative energy and energy efficiency to fusion, hydrogen and superconductor technologies.
Newest articles

Long-sought structure of powerful anticancer natural product
…solved by integrated approach. A collaborative effort by the research groups of Professor Haruhiko Fuwa from Chuo University and Professor Masashi Tsuda from Kochi University has culminated in the structure…

Making a difference: Efficient water harvesting from air possible
Copolymer solution uses water-loving differential to induce desorption at lower temperatures. Harvesting water from the air and decreasing humidity are crucial to realizing a more comfortable life for humanity. Water-adsorption…

In major materials breakthrough
UVA team solves a nearly 200-year-old challenge in polymers. UVA researchers defy materials science rules with molecules that release stored length to decouple stiffness and stretchability. Researchers at the University…



