Scientists find a way to stabilize a promising material for solar panels
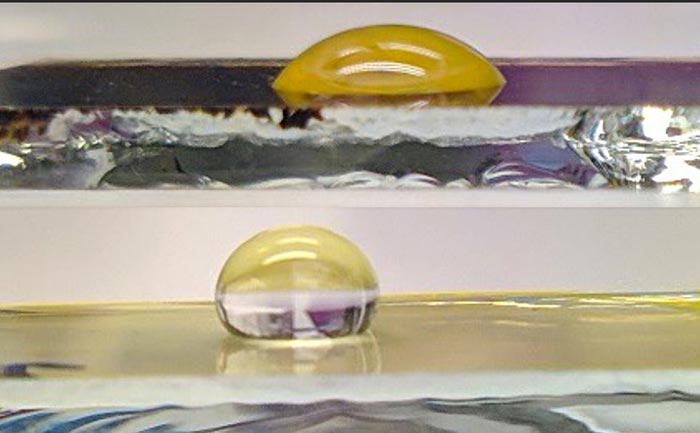
This image shows the difference between an ordinary perovskite solar cell, top, and a perovskits solar cell with a water-repellent molecular-thin layer, below.
Credit: James Gardner/KTH Royal Institute of Technology
One of the solar energy market’s most promising solar cell materials—perovskite—is also the most frustrating. A research team in Sweden reports a possible solution to the environmental instability of perovskite—an alternative to silicon that’s cheap and highly efficient, yet degrades dramatically when exposed to moisture.
The team, from KTH Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm, developed a new synthetic alloy that increases perovskite cells’ durability while preserving energy conversion performance. The researchers published their findings in Nature’s Communications Materials.
“Perovskite usually dissolves immediately on contact with water,” says co-author James Gardner, a researcher at KTH. “We have proven that our alloyed perovskite can survive for several minutes completely immersed in water, which is over a 100 times more stable than the perovskite alone. What’s more, the solar cells that we have built from the material retain their efficiency for more than 100 days after they are manufactured.”
Perovskites are a class of materials with a specific crystal structure, named after the mineral with that structure. In solar cells they have shown potential for high performance—with energy conversion efficiencies as high as 25 percent—and, best of all, low production costs.
However these thin-film cells are highly susceptible to outdoor elements, which accelerates their degradation—and limits their viability in a solar market where virtually all panels are based on silicon.
KTH researcher James Gardner says that his team’s work represents a step towards developing an alternative, more stable perskovite product. They encapsulated a light-absorbing perskovite layer with a 2D perskovite film layer that provides a water repellent quality thanks to the addition of long-chain alkylammonium ions.
The researchers report that the cells’ power conversion efficiency dropped by 20 percent after six months at a relative humidity of 25 to 80 percent; and they could be completely immersed in water for a few minutes before degradation started.
Gardner says that the 2D perovskite coating also mitigates energy losses in the light-absorbing 3D perovskite, which leads to an enhancement in the photovoltage. The findings indicate that long-chain alkylammonium cation-based 2D perovskites can improve the environmental stability of 3D-based perovskites, without significant loss of performance and may lead to commercially successful perovskite solar cells.
Moisture tolerant solar cells by encapsulating 3D perovskite with long-chain alkylammonium cation-based 2D perovskite
Communications Materials
Kore, et al.
23 September 2021
DOI https://doi.org/10.1038/s43246-021-00200-8
Journal: Communications Materials
DOI: 10.1038/s43246-021-00200-8
Method of Research: Experimental study
Article Title: Moisture tolerant solar cells by encapsulating 3D perovskite with long-chain alkylammonium cation-based 2D perovskite
Article Publication Date: 23-Sep-2021
COI Statement: Researchers report no conflict of interest.
Media Contact
David Callahan
KTH, Royal Institute of Technology
callahan@kth.se
Office: 0737650593
All latest news from the category: Power and Electrical Engineering
This topic covers issues related to energy generation, conversion, transportation and consumption and how the industry is addressing the challenge of energy efficiency in general.
innovations-report provides in-depth and informative reports and articles on subjects ranging from wind energy, fuel cell technology, solar energy, geothermal energy, petroleum, gas, nuclear engineering, alternative energy and energy efficiency to fusion, hydrogen and superconductor technologies.
Newest articles

You are What You Eat—Stanford Study Links Fiber to Anti-Cancer Gene Modulation
The Fiber Gap: A Growing Concern in American Diets Fiber is well known to be an important part of a healthy diet, yet less than 10% of Americans eat the minimum recommended…

Trust Your Gut—RNA-Protein Discovery for Better Immunity
HIRI researchers uncover control mechanisms of polysaccharide utilization in Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. Researchers at the Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based Infection Research (HIRI) and the Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) in Würzburg have identified a…

ASXL1 Mutation: The Hidden Trigger Behind Blood Cancers and Inflammation
Scientists show how a mutated gene harms red and white blood cells. LA JOLLA, CA—Scientists at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) have discovered how a mutated gene kicks off…



